Strategic planning and the role of teaching and learning
Distilling hundreds of comments about the future of the university into something manageable and meaningful is, in understated terms, a challenge.
The university’s department of Analytics and Institutional Research accomplished that, though, creating a 73-item list that summarizes ideas from a fall planning session and from comments submitted through an online portal. That list, titled What We Could Do at KU, was distributed to the 150 or so university employees who gathered last week for a second strategic planning session. Presumably, Provost Barbara Bichelmeyer and Chancellor Doug Girod drew on those in creating another document that listed vision, mission and values statements, along with their institutional priorities. The priorities they laid out – student success, healthy and vibrant communities, and research and scholarship – offer a good sense of where they want the university to go in the coming years.

I have a few thoughts about those priorities – namely a lack of any mention of teaching – but I want to focus on something else first.
I found many connections among the 73 suggestions on the What We Could Do list, and I wanted a way to get a better grasp on those ideas. That’s because they provide a broad look at what employees around the university see as important.
I started by creating a spreadsheet, combining and paring the 73 suggestions into 68 words and short phrases. Think of it as a summary of a summary, which has both benefits and drawbacks. I then used those to create the two word clouds that accompany this article.
I wasn’t able to get all 68 words and phrases into a single word cloud, so I eliminated those that were mentioned by fewer than five people. I also created a separate list of 11 verbs that were used in the summary statements. Most describe a need to do more or less of something. This by no means indicates a consensus of ideas from around campus. Rather, it represents the opinions of those who were willing to take the time to attend a planning session or to submit comments online. (I was one of those people.)
Collaborate and communicate
There’s nothing startling on the list, but I was nonetheless surprised by the prominence of collaboration and communication. I agree with those wholeheartedly, and I’m glad others put them at the top of the list.
In far too many cases, departments and offices work in isolation (or in siloes, another word on the list) and even compete against one another for students, resources and attention. To improve as a university, we must find more ways to work together and see ourselves as part of a singular effort rather than as a collection of competing entities. We need to find more ways for our students to collaborate with faculty and with one another. We also need to collaborate with other colleges and universities, and with communities in Lawrence, Kansas City and across Kansas.

Doing that requires better communication internally and externally. We have to make sure potential partners around the university know what we are doing, and we need to tell our story (another prominent term) to students, families, businesses and communities. They need to understand that we are part of – not separate from – them.
Another frequently mentioned issue, financial stability, ties into other needs like maintenance, retention, accessibility, professional development, degree cost, campus beauty, mental health, morale, accountability and transparency.
Three other prominent terms on the list – diversity, mental health and generational needs – tie closely together. The diversity of the student body has increased over the last decade, but the student population at KU is still predominantly white. The faculty and staff are even less diverse. The current generations of students are more diverse and have different needs from previous generations.
Not surprisingly, most of the comments from around campus called for an increase in something, including diversity, revenue, accountability, prestige, student and faculty retention, and, of course, collaboration and communication. After years of underfunding and a few rounds of budget cuts, there are many unmet needs.
What about teaching?
If the What We Could Do at KU list represented the opinions of faculty and staff, a document called Jawhawks Rising gave a clear sense of where university leaders want to go. It’s a good aspirational document.
Strangely missing, though, is any mention of teaching. The document uses phrasing like “community of learners,” and “student engagement” and “educate leaders.” It lists “student success” as one of three core institutional priorities.
Teaching doesn’t show up anywhere, though. That’s discouraging and disturbing. You can argue that “educate” involves teaching. It does. But without a clear strategy for improving and elevating the importance of teaching, any attempt to improve student success will fall short. And without the involvement of faculty in student success, the vision, the mission and the values of the institution quickly become hollow.
All of this is a work in progress, and encouragingly, Bichelmeyer gave teaching an important nod in remarks she made at the start of the strategic planning session last week.
“We’re learning about how we teach and how our students learn,” Bichelmeyer said, referring to the use of analytics to examine curricula and student movement through curricula. “There are lots of ways where we can start to unpack the individual student from the crowd through watching and knowing that they need a nudge to say, ‘It’s really important for you to get to the first week of class’ or ‘It’s really important that you don’t turn your homework in late.’ ”
She added: “We’re not teaching little widgets on an assembly line where we hold time constant and let achievement vary or we think about our work as production.”
She also pointed to the need to change our approach to engaging students, many of whom work 20 or more hours a week and have family responsibilities. They also see technology as an important part of who they are.
“Students would rather have a lecture on YouTube than sit in a class with a thousand students where they can’t see the professor and they can’t see what’s on the board and they maybe can’t hear,” Bichelmeyer said. “And they don’t have to pay for parking, and they don’t have to get a babysitter, and they can do that at night.
“So when we think about unbundling the elements of instruction, we have to understand that what we do well at the University of Kansas that nobody else can do is we engage students,” she added.
Unbundling and rethinking
Additionally, she said, digital technology is leading to the separation of teaching from certification. That is, students no longer need a university credential to get good jobs. They can learn from many online providers or gain skills from short-term coding camps and other intensive sessions that don’t require a four- or five-year commitment and cost far less than a university degree.
“So we have to think about what it is that only we can do really well and how we think about the educational experience from the students’ perspective in order to help them think about why it’s worth it for them to be at KU,” Bichelmeyer said.
Think collaboration, communication, diversity, generational needs, networking, accessibility, engagement, cost and other terms from the campus list. But also think teaching and learning, which is why students come to the university in the first place.
ed to collaborate with other colleges and universities, and with communities in Lawrence, Kansas City and across Kansas.
As challenges mount, higher ed looks in new directions
WASHINGTON – As colleges and universities prepare to encounter what has become known as a cliff in traditional student enrollment, they are looking for ways to reach out, branch out, and form partnerships that might once have been unthinkable.
 That desire to branch out was clear from the sessions I attended at the annual meeting of the Association of American Colleges and Universities. For instance, speakers at the conference urged colleagues and their universities to:
That desire to branch out was clear from the sessions I attended at the annual meeting of the Association of American Colleges and Universities. For instance, speakers at the conference urged colleagues and their universities to:
- Do a better job of working with community colleges, whose lower cost is appealing to students, most of whom want to continue at four-year institutions.
- Reach out to high school students and introduce them to liberal education before they choose a college and a major.
- Draw in older adults, reintroduce them to learning as they move into a new phase of life, and draw on their expertise in classes and career development.
- Create stronger partnerships with other colleges and universities.
- Create better strategies for telling the story of higher education.
There’s no secret about why branching out is important. At a session titled “Responding to the Crisis in Higher Education,” Elaine Maimon, president of Governors State University in Illinois, said “crisis” had appeared in AAC&U session titles nearly every year in the decades she had been attending the conference. (Maimon was facing her own crisis back home.) Even so, she said:
“I’m ready to say the revolution is here.”
‘Stop rehearsing our dilemmas’

I’ve written considerably about the idea of “revolution” in higher education, about the need for universities to adapt and change, and about the plodding approaches that higher education as a whole has taken to the broad challenges.
In short: The number of traditional students is declining, especially in the Midwest and Northeast. Demographic shifts have created what one AAC&U participant called “a new student majority” made up of first-generation students, students of color, adults, and military veterans, and many of those students start at community colleges. State and federal funding has plummeted. And digital technology has created what Maimon called “an epistemological revolution in terms of ways of knowing.”
Mary Dana Hinton, president of the College of Saint Benedict, said colleges and universities needed to stop “stop rehearsing our dilemmas” and work at making changes.
“We know what our problems are,” Hinton said. “We need to change, and to invest in our faculty, our staff and our leadership so that we create environments and spaces where every student on our campus can see themselves, can feel appreciated, can be challenged and transformed, and that we as institutions are transformed by the students who come to us.”
The sort of transformation that Hinton referred to has many components.
Working with community colleges
Scott Jaschik, editor of Inside Higher Ed, emphasized the importance of making connections with community colleges because “that’s where the students are.”
Most Americans who earn a bachelor’s degree start at community college, Jaschik said, and four-year institutions need to make transfer easier and create welcoming environments for community college students. Some states are also making community college free, he said, an idea that has transcended political ideology.

Cost is playing a big part in students’ decisions. Al Newell of the education research company EAB said that the lower cost of community colleges had great appeal to Generation Z, which he described as thrifty and frugal. More than 40% of students whose families earn at least $250,000 a year are considering community colleges, Newell said, with some looking at college as a seven- or eight-year investment if students go to graduate school.
Twenty years ago, he said, students aspired to attend the best school they could get into. Now, he said, students’ mindset is that they will go to the best school that they can get into and that their families can afford.
An announcement last week underscored the importance of community colleges. Southern New Hampshire University, a large provider of online education, offered students of Pennsylvania’s community colleges a 10% tuition discount, a move that is expected to draw students away from the state’s four-year institutions.
A different approach to adult education
A new model for bringing adults into college courses has begun to emerge.
Colleges and universities have offered continuing education classes for adults and retirees for many years. Since the early 2000s, KU and many other universities have been involved in the Osher Lifelong Learning Institute, which focuses on adults age 50 and older. What’s different this time is that universities are creating longer and more intensive programs for older adults, integrating them into traditional classes and activities, and using their expertise to enrich discussions and career preparation.
Longevity is changing workers’ outlook, and many of those in the baby boom generation are looking for new paths after they retire, Kate Schaefers, executive director of the Advanced Careers Initiative at the University of Minnesota, said during an AAC&U panel discussion. Minnesota is one of several universities that have created programs for late-career or retired professionals. Many of those are modeled on Stanford’s Distinguished Careers Institute, which brings in a small cohort each year and helps each participant shape an individual curriculum built on their interests. It integrates them into traditional classes but also creates separate seminars, colloquia and other events. That approach has been successful enough that Stanford is planning to create a non-profit organization to help universities create similar programs, participants at an AAC&U panel said.
Organizers use words like “transformative” to explain the rich opportunities these new programs provide and the powerful bonds they create. The programs are also expensive: often $60,000 a year or more. Most programs offer financial aid for a few fellows, but organizers say the cost reflects the need to be self-sufficient.
Reaching out in other ways
Conference panelists talked about the need to reach out to many other constituencies, including businesses, rural students, low-income students, students of color, non-traditional students, and international students, whose numbers have declined over the past few years.
Colleges and universities start sending promotional material to prospective students early in high school. Later on, they encourage families to tour campuses and to talk with advisors. Those approaches help get a school’s name in students’ mind and help students get a sense of a school’s atmosphere. What they fail to do, though, is to help students understand what happens within a particular discipline.

Andrew Delbanco, president of the Teagle Foundation and a professor at Columbia, said universities needed to create opportunities to bring high school students – especially those from underserved populations – to their campuses for a week or more and engage them in intensive humanities seminars that explore the depth and breadth of liberal education. That approach, which Teagle has been funding, helps students “learn that college is not only about getting a job.” It also helps faculty members, graduate students and undergraduates better understand the perspectives of underserved students.
“We all agree in this room about the value of liberal education,” Delbanco said. “But we have a problem. You cannot explain the value of liberal education to someone who hasn’t had one. You can’t do it. … You cannot convey the taste of honey to someone who hasn’t tasted it.”
The importance of that type of approach was reinforced by statistics at Newell’s session. A survey of 5,200 students at Chicago public schools found that in ninth grade nearly all students aspired to college. By the 11th grade, that dropped to 72%. By 12th grade, 59%. In the end, only 41% enrolled in college.
He cited many reasons for the drop-off: lack of role models who have gone to college; exclusion from advanced placement classes; lack of understanding of the enrollment process; failure to take required courses; and lack of money.
“The reality is that the way we do business is going to have to adapt,” Newell said.
He gave several examples of how colleges and universities were adapting. One of the most prominent is through partnerships with or acquisitions of other institutions. In some cases, university systems are requiring consolidation. In others, a university acquires a nearby struggling institution in what Newell describes as a “goodwill grace merger.” In still others, the acquisitions are pure business deals, or “strategic capital asset acquisition,” as Newell described them. (Think of Purdue’s purchase of Kaplan.)
We also need to keep lobbying skeptical legislators and talking more to a skeptical public, Delbanco said — and working more closely with local communities.
It’s a daunting challenge, but AAC&U sessions seemed far more upbeat than they have been in the past few years, even as Delbanco summed up an admonition that was repeated by several others:
“Colleges and universities must serve young people – and not only young people – beyond their gates more effectively,” he said.
Doug Ward is the associate director of the Center for Teaching Excellence and an associate professor of journalism. You can follow him on Twitter @kuediting.
How a living syllabus can lead to continual improvement in a course
By Doug Ward
The end of a semester is always hectic, but it’s important to spend time reflecting on your classes while things are still fresh in your mind.
Did students learn what you had hoped? If not, what do you need to change the next time you teach the class? What activities or assignments led to unexpected results or fell short of your expectations? What readings did students struggle with and how can you help students grasp them better? What discussion areas resulted in a mostly silent classroom? What elements of your syllabus did students find unclear and need revision?
Those are just a few things to consider. Now is good time to make some notes because by the time you get to a chapter or assignment or module or discussion next time, you will struggle to remember exactly what changes you had planned to make.
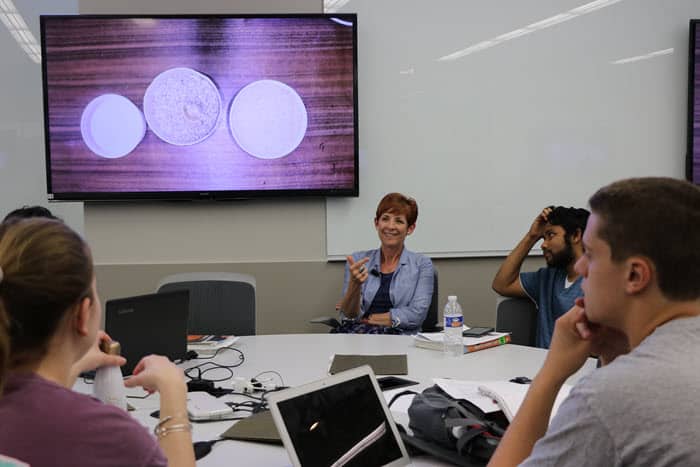
Ashley Herda, assistant professor of health, sport and exercise sciences, has found a great way to reflect on her teaching and to make sure she is ready the next time she teaches a class. She calls it a living syllabus.

Herda explained her approach during a workshop at the Edwards Campus last week. She said the living syllabus worked like this: After she distributes the course syllabus to students, she sets aside a copy for herself and makes digital notes on it during the semester. If students find something unclear, she makes changes in the syllabus in edit trace immediately. If an assignment takes far less time than she expected, she highlights a section of the syllabus and makes notes in bubbles to the side. If there are problems in grading, she reminds herself right in the document.
This approach makes it easy for her to make adjustments for a future class, she said. Rather than starting from scratch each time, she has the living syllabus ready to go.
I love the idea of a living syllabus. The name perfectly captures the idea of a course in a state of constant improvement. It also turns the syllabus into a means of reflection, not just an artifact of a class.
During the workshop, other instructors explained their own approaches to reflection and course improvement. John Bricklemyer, lecturer in engineering and project management, jots down notes after each module in the online classes he teaches and frequently shares his thoughts with other instructors. Lee Stuart, leadership programs manager on the Edwards Campus, includes a reflection component for each assignment that asks students for their feedback on the assignment. That helps him get a better sense of places where students are struggling or of assignments that might be too easy or that are not meaningful.
Like others, I have long made notes about classes and assignments during the semester. I usually do this in a OneNote file where I keep a class outline, readings and notes. I also build in reflection assignments in each course I teach and ask students to evaluate themselves and the course. When I teach in person, I usually spend part of the last day of class talking with students about the strengths and weaknesses of the class. I’m candid about strong and weak areas I saw in the course and students are generally forthcoming with their own thoughts.
The method of reflection on a course is less important than the act of reflecting, though. The disciplines we study and the courses we teach are dynamic and need continual oversight. Students change. Materials change. Our understanding of the subject matter changes. Needs of a department change.
Imagine how vibrant teaching might be if all instructors embraced the philosophy of a living syllabus. It’s a worthy aspiration.
Guidelines for successful brainstorming
A recent article from Innovation Excellence offered what it called the four rules of brainstorming. The idea of rules for something as freewheeling as brainstorming seems a bit odd, but I can see the logic in establishing some guidelines.
Innovation Excellence attributed the rules to Alex Osborn and his book Applied Imagination, published in 1953. Here they are:
- Go for quantity over quality, because we know the best way to get good ideas is to just start with lots of ideas.
- Withhold criticism, or “no idea is a bad idea.”
- Encourage wild ideas; just freewheel and go crazy? (Sort of the point of rule two.)
- Combine and improve upon ideas.
After a ‘train wreck’ of a start, Geology 101 helps redefine student success
Jennifer Roberts doesn’t hold back when describing her first attempt at active learning in a large lecture course.
“It was a train wreck,” said Roberts, a professor of geology who is now chair of the department. “It was bloody. Students were irate.”

This was in Geology 101, a required course for geology majors and one that typically draws a large number of engineering students. Starting in 2013, Roberts worked with a post-doctoral teaching fellow, Kelsey Bitting, to transform the class. They cut back on lecturing and devoted more time to group discussion and guided inquiry, with worksheets and in-class problem-solving. They introduced weekly reading quizzes and in-class questions to gauge understanding. They had students do more out-of-class writing. They also adopted two-stage exams and eliminated multiple-choice questions.
Essentially, she said in an interview in 2014, they made “this a class about the work students put into it and not necessarily about who had the old test that they memorized or just who was good at taking tests.”
Geology 101 is just one of hundreds of classes that have been transformed over the past few years as the university has emphasized the importance of retaining more students and helping them graduate. It illustrates, though, the hard work that has gone into raising retention and graduation rates at KU.
This fall, 86.2% of last year’s freshman class returned, compared with a low of 77.8% in 2008. That’s a phenomenal accomplishment made possible by the work of everyone from instructors like Roberts who have adopted more effective teaching practices to advisors who have helped students make better choices to administrators who have created new support programs and allocated money and resources to address a collective problem. These changes have helped shift the culture of teaching to one that emphasizes learning for all students.

Geology 101 also illustrates the importance of shared responsibility and community building in the success of students. For instance, Roberts’ remake of the course involved a teaching fellow, a second instructor, graduate teaching assistants and several undergraduate teaching assistants. The second instructor has been crucial for maintaining continuity because that person becomes the lead instructor in the ensuing semester. Noah McLean, Andreas Möller and Craig Marshall, among others, have been instrumental in maintaining that continuity and in continuing the evolution of Geology 101.
Having multiple instructors and teaching assistants in a classroom allows for group work, makes it easier for students to ask questions and get help with challenging course material, and makes large classes much more personal. New classrooms in the Earth, Energy and Environment Center and the LEEP2 engineering building have improved the atmosphere, too. The rooms in those buildings are in high demand, largely because their layout promotes interaction and makes large classes feel smaller than those in the stadium-style seating of Budig Hall.
McLean, an assistant professor of geology, said that the traditional layout for large classrooms intimidated many students and dissuaded them from asking questions. In active-learning classrooms, “you’re only looking at eight other people, and it’s much easier to bring students in and have a class-wide discussion,” McLean said.
‘Equity between men and women’
The series of changes made in Geology 101 has worked. Despite student complaints, more started getting C’s rather than D’s. Underrepresented minority students made substantial gains, with the number receiving D’s or F’s or withdrawing falling 5.6% between 2009 and 2016 even as more underrepresented students took the class.

More impressively, women in the class began performing significantly better in that same metric (a decline of 9.5%). Roberts said that women often accounted for 80% of the students who withdrew from the class or received D’s or F’s. In 2017, she said: “We now have equity between men and women.”
The work isn’t done, either in Geology 101 or in other classes across the university. In many ways, it has only begun, and we have a long way to go to achieve the type of widespread equity and achievement we hope to see. We should definitely celebrate, but we still have to keep pushing.
A year after remaking Geology 101, Roberts offered this reflection:
“The advice I have been giving the people who have started, especially in designing courses from scratch with this, is to make sure that they are choosing topics that they are really excited about because this can be a grind,” Roberts said. “And if you’re not really excited about going to class and sharing that information with the students, I don’t think you’re going to do it very well.”
A Harry Potter education model for a ‘Hunger Games’ generation?
I’ve been doubtful about the emergence of a Generation Z. Strangely, Harry Potter and Katniss Everdeen, along with some reassurances from Pew Research, have me reconsidering.
Before I get to Hogwarts and District 12, though, I need to provide some background.
A few years ago, two of my students, eager to look behind the hype of marketers who claimed to see into the minds and habits of a post-millennial generation, came away frustrated. After semester-long research projects, they both asked the same questions: Who can really define a generation? And is “generation” just a convenient label that older people apply to younger people they don’t understand?
A baby boom generation made some sense because it was part of a demographic shift, the students said. Yes, today’s students are certainly different, but the “generation” labels that have been applied seem more of a put-down than an amalgamation of meaningful, or valid, characteristics.

Michael Dimock of the Pew Research Center explained some of the haziness of generational labels earlier this year when he wrote that Pew researchers were adopting the Generation Z category in their work. He wrote:
“Generational cutoff points aren’t an exact science. They should be viewed primarily as tools” for analyzing views on things like work, education, social issues and politics. Pew defines Generation Z as anyone born in 1997 or after. Others see Generation Z as starting earlier, and some place the starting point as late as 2005. By most definitions, though, traditional college-age students now consist solely of Generation Z, and the oldest in that group have already graduated.
What does that mean?
I thought about my students’ search for Generation Z as I listened to speakers at the Educause 2019 conference in Chicago recently. My students’ questions were – and still are – valid. Their search for a Generation Z may just have been a few years premature, though.
The racial and ethnic diversity of this generation — and how that diversity shapes views and expectations — has rightly received considerable attention. At Educause, though, the father and son team of David and Jonah Stillman made a case for “generational personalities,” which they said formed from experiences in adolescence. Many of those experiences are tied to significant economic and cultural events. Here are a few of the characteristics that the Stillmans said separated millennials from Generation Z.
Millennials
- Came of age during an economic boom.
- Parents, mostly baby boomers, told them they could do anything.
- Went through childhood during what the Stillmans called “the self-esteem movement,” when everyone got a trophy just for participating.
- Parents preached a message of college at any cost – apparently even to themselves – and told their children they could change the world.
- Jobs were about seeking meaning and changing the world.
- Technologically minded but with a clear separation between online and in person.
Generation Z
- Came of age during and after the 2007-2008 recession, when their parents’ net worth plummeted and they saw seemingly unsinkable companies barely able to stay afloat.
- They are realists. Their parents, mostly from Generation X, emphasized the need to compete and win. (If you doubt this, just do a search for “TikTok famous.”)
- Watched as millennials took on enormous debt to pay for college, even as many employers started to emphasize skills rather degrees.
- Jobs are about money. Full stop.
- See few boundaries between physical and digital. (Think Pokemon Go.) They even saw online companies begin to create physical stores, another case where they see “no line at all” between online and in person.
Even popular culture icons offered competing messages. Millennials read about and watched Harry Potter, a young wizard with a tight group of friends who grappled with the meaning and purpose of their magic powers. Generation Z read about and watched Katniss Everdeen, a young rebel in a dystopian nation who is chosen for a fight to the death in The Hunger Games. The message: one against the world; win or die; children are expendable.
This is all a broad-brush picture, of course, but I find that much of it rings true. After all, enrollment in business schools has soared as enrollment in the liberal arts has declined. Many students are working 20-plus hours a week to help pay their college bills. They want flexibility in their schedules and access to technology always. Most students and parents still see value in college, but they look closely at price and consider their return on investment.
So what does this mean for higher education? The Stillmans offered these observations and suggestions:
Get on their radar earlier
Many of these students are trying to make college and career decisions much earlier than previous generations did. They crave certainty and security in their careers. Universities that tap into that desire for a clear pathway have a better chance of reaching those students than those that wait. Relatedly, these students want to know what universities have to offer. They seek out winners and opportunities, and they want to see that reflected in their schools.
Group work is harder
This generation is competitive. They want to stand out and they resent others who tag along in group projects and don’t work as hard as they do. That means they dislike group work, even though the ability to collaborate is among the top skills that employers seek. That means, the Stillmans said, that educators will have to work harder to help these students learn group skills.
So is traditional communication
Older adults complain that this generation is illiterate, David Stillman said. He argued, though, that today’s students are writing more than ever. They post on social media and in online forums. They chat via instant messages and games. They are in constant conversation. Much of that may be in the form of “lol” and “omg,” Stillman said, “but who are we to say that’s not writing?” They also learned to communicate with emojis before they communicated in words, he said. That approach creates more ambiguity and leaves more room for interpretation, he said. So students need help understanding how to communicate in a professional world. Even so, he said, “professors need to understand emojis.”
Emphasize the tangible
Promoting vague “experiences” and learning for learning’s sake doesn’t work for most of these students. Rather, they want to see the practical application and individual benefit of their school work. That means instructors and advisors need to explain why students are learning what they are learning and how the various disciplines, activities and assignments fit together and help lead to good jobs. Additionally, universities, departments and classes should partner with businesses, David Stillman said. Bring professionals from various fields to campus so that students can learn about pathways and make connections between what they are learning and what they might do on the job.
Allow customization
A higher percentage of Generation Z was home-schooled, and many of their parents are entrepreneurs. They are open to alternative paths to learning, and they value customization. After all, Amazon and Netflix know what they want and make frequent suggestions about what they should buy or watch. Why shouldn’t their college? Iowa State, which caught on to this earlier than most universities, sends out video announcements for each student. These videos include a “breaking news” announcement by a CNN anchor, a message from the college president and the football coach, a shot of a banner with the student’s name, and footage of thousands of students cheering and celebrating. (Some students apply to Iowa State just to get a video, the Stillmans said.) Other schools have allowed students to create custom majors, a strategy that all schools need to adopt, the Stillmans said.
Improve online courses
Students still prefer in-person courses, but they want the flexibility that online courses provide. That flexibility is critical for a generation that is putting in more hours on jobs to pay for college. They also expect online courses to have the same quality and the same outcomes as in-person courses. The culture, the feel, the layout of an online course should be the same as an in-person course, the Stillmans said. Everything should be seamless.
Be flexible with technology
Students in Generation Z “don’t see the difference at all” between the physical and digital worlds. Technology is simply part of who they are. It connects them. It informs them. They expect it to be there. Universities that demonstrate technological sophistication will have an advantage, the Stillmans said. That doesn’t mean Generation Z is impressed by technologically advanced campuses. That is simply an expectation. These students take that expectation into the classroom, too. Instructors who ban this technology simply stoke students’ fear of missing out on something online. So rather than take that technology away, help them learn how to use it to learn.
Those are just a few of the few of the student characteristics we need to pay attention to. Yes, these are broad generalizations that don’t apply to all students, but they help us understand some of the challenges we face as educators. College used to have a Harry Potter-like magic in attracting students, but it has entered a world much more like The Hunger Games. We can still be suspicious of labels like Generation Z – I still am – but we need to adjust to the reality of the changes.
Enrollment numbers reflect a difficult decade for higher education (and provide a few surprises)
Enrollment at Kansas regents universities declined again this year. I say again because enrollment has declined each year since 2011.
The decline – 5.7% since 2011 — is relatively small, but it illustrates the challenges of a state university system that has become increasingly dependent on student tuition dollars to finance operations. It also illustrates the challenges that regents universities will face in the next decade as the number of traditional college-age students flattens after a post-recession “baby bust.”
The National Center for Education Statistics projects that undergraduate enrollment nationwide will increase about 3% by 2028, but that national average blurs regional differences. Institutions in the Midwest and Northeast are especially vulnerable. Many smaller colleges have faced growing economic problems, with some merging and more than 20 closing.
KU isn’t in any immediate danger from those trends, but the regents system as a whole is. Given the current political climate, it seems likely that Kansas will face some of the same pressures that states like Wisconsin and Alaska have faced to close or merge campuses.
In Kansas, Wichita Area Technical College merged with Wichita State two years ago, a move that made sense given their proximity. It isn’t much of a stretch to imagine financial concerns forcing additional mergers – mergers that would be much more painful than the one in Wichita. Eleven of the state’s community colleges have had double-digit enrollment declines over the past five years, and three – Cowley, Allen and Highland – have seen enrollment fall by more than 20%. Even Johnson County Community College, the largest in the state, isn’t immune from this trend. Its enrollment has declined 7.8% over the past five years, although there was a slight uptick this year.
I’m not trying to predict impending doom. Rather, I see the numbers as a clear signal of the need to move quickly with innovative approaches that better meet the needs of a changing student population. Colleges and universities can no longer expect student applications to simply flow in with regularity. They must find niches that set them apart, form partnerships across disciplines and institutions, do more to reach out with online courses, and develop new approaches that make a college education more of an ongoing process – and one of individual renewal – than a degree-and-done-forever approach.
The numbers at KU
KU’s full-time equivalency enrollment fell slightly this year. As you can see from the chart above, though, there has been only slight movement over the past six years. That’s mostly good news, especially because retention rates have increased. This fall, 86.2% of last year’s freshman class returned, and retention of freshmen has increased substantially since hitting a low of 77.8% in 2008.
That’s a phenomenal accomplishment made possible by the work of everyone from instructors who have adopted more effective teaching practices to advisors who have helped students make better choices to administrators who have created new support programs and allocated money and resources to address a collective problem.
The university did a good job of highlighting other aspects of this fall’s enrollment report, so I won’t go into those. I would like to touch on some other trends I saw in the enrollment figures. These figures come from various reports and public dashboards on the site of Analytics and Institutional Research. Wherever possible, I have used full-time equivalency figures rather than headcount. The regents and the federal government have shifted to full-time equivalency because it cuts down on possible distortions from part-time enrollment and allows for a better comparison across universities. The university tends to prefer headcount.
Troublesome long-term trends
Combined enrollment at the Lawrence and Edwards campuses has been mostly stable over the past few years. The longer-term trends aren’t as positive. Enrollment has declined 10.5% since 2007 and 13% since a peak in 2008.
For KU as a whole, those declines have been partly offset by a growth of 11.2% at the medical center since 2014. Enrollment at the Edwards Campus has grown in each of the past four years but is 11% below where it was in 2011.
Not surprisingly, the largest decline in the student population has been in the College of Liberal Arts and Sciences. It still has the largest number of students by far of any college at KU, but undergraduate enrollment has fallen 21.6% since 2010, and graduate enrollment has fallen 18.2%. The largest percentage gains in undergraduate enrollment since Fall 2010 have been in business (up 122%) and engineering (up 46.3%).
Interestingly, the largest percentage increase overall was in non-degree-seeking students, whose numbers have risen 181% since 2010. There were 491 of those students this fall. That’s a small number in the overall enrollment picture, but it clearly shows an interest among a group that is rarely discussed when we talk about enrollment.
Shifting gender balance
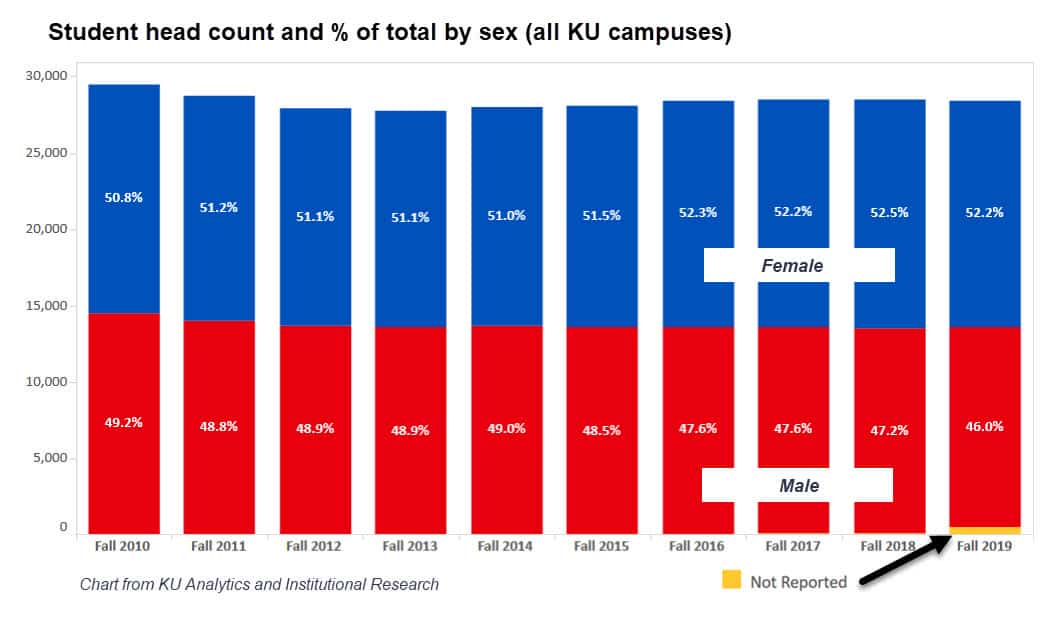
Men accounted for 46% of KU students this fall, the lowest percentage of the decade. The number of men enrolling at KU has declined from 49.2% in 2010, reflecting a national trend of fewer men going to college.
The number of students not reporting gender spiked this year to 524 from 75 in Fall 2018, 53 in Fall 2017 and 25 in Fall 2016. This reflects a national trend of students more willing to identify as gender fluid, transgender or non-binary.
Interestingly, the vast majority of those who did not report gender were graduate students. The breakdown of graduate students this fall is 50.6% women, 40.4% men and 9% not listing gender.
Other changes in student demographics
Several other changes in the characteristics of students are worth noting:
- Declining number of transfer students.Transfer students have never made up a large percentage of the student population at KU, but their numbers have fallen significantly during the past decade. In Fall 2010, the Lawrence campus reported 1,404 transfer students, compared with 1,024 this fall. That is a decline of 27%.
- Declining number of graduate students. The Lawrence campus has 5,570 graduate students this fall, a decline of 9.5% since 2016 and 13.5% since 2010. This is largely a result of a smaller number of students pursuing a master’s degree (down 19.8% since 2010), although the number of doctoral students has declined 9.1% from a peak in 2013.
- Declining number of international students. The number of international students fell for the fourth straight year and is now 14% below a peak of 2,363 in Fall 2015. This again follows a national trend.
- Rising number of Hispanic students. The number of Hispanic students attending KU has increased 65% since 2010, with growth in every year this decade. Hispanic students now make up 8% of the student body. This again reflects national trends.
- Rising number of part-time students. The number of part-time students on the Lawrence and Edwards campuses surpassed 4,000 for the first time this fall. Part-time students now account for 16.3% of the total student population, the highest percentage this decade and up from 13.7% in 2012.
Changes at Edwards Campus
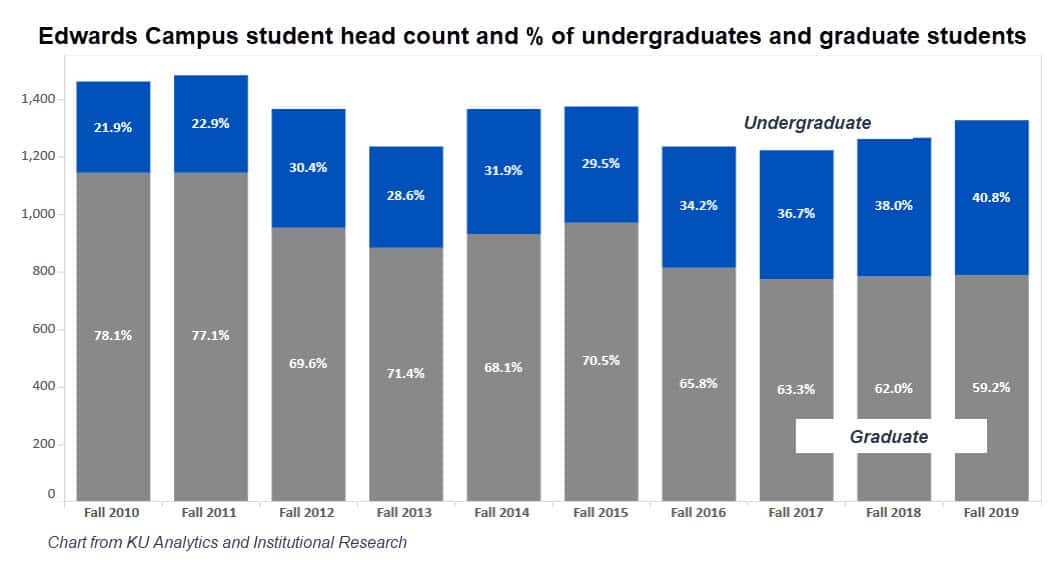 KU’s Edwards Campus has traditionally been reliant on professional master’s programs for its enrollment. That has begun to shift toward more of a balance of graduate and undergraduate programs.
KU’s Edwards Campus has traditionally been reliant on professional master’s programs for its enrollment. That has begun to shift toward more of a balance of graduate and undergraduate programs.
Undergraduates now account for nearly 41% of students at the Edwards campus, nearly double the percentage of a decade ago. That is an enormous shift in mission and mentality. The campus is still heavily reliant on working professionals who attend evening classes, but it has increased its online offerings, partnered with Kansas City-area schools and businesses, and drawn undergraduates to programs like information technology, molecular biosciences and exercise science.
A national conversation on evaluating teaching starts to take shape
A recent meeting at the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering and Medicine achieved little consensus on how best to evaluate teaching, but it certainly showed a widespread desire for a fairer system that better reflects the many components of excellent teaching.
The National Academies co-sponsored the meeting earlier this month in Washington with the Association of American Universities and TEval, a project associated with the Center for Teaching Excellence at KU. The meeting brought together leaders from universities around the country to discuss ways to provide a richer evaluation of faculty teaching and, ultimately, expand the use of practices that have been shown to improve student learning.

My colleague Andrea Greenhoot, professor of psychology and director of CTE, represented KU at the meeting. Members of the TEval team from the University of Massachusetts, Amherst, the University of Colorado, Boulder, and Michigan State University also attended. The TEval project involves more than 60 faculty members at KU, CU and UMass. It received a five-year, $2.8 million grant from the National Science Foundation last year to explore ways to create a fairer, more nuanced approach to evaluating teaching.
The TEval project, which is known as Benchmarks at KU, has helped put KU at the forefront of the discussion about evaluating teaching and adopting more effective pedagogical strategies. Nine departments have been working to adapt a rubric developed at CTE(Link does not exist), identify appropriate forms of evidence, and rethink the way they evaluate teaching. Similar conversations are taking place among faculty at CU and UMass. One goal of the project is to provide a framework that other universities can follow.
Universities have long relied on student surveys as the primary – and often sole – means of evaluating teaching. Those surveys can gather important feedback from students, but they provide only one perspective on a complex process that students know little about. The results of the surveys have also come under increasing scrutiny for biases against some instructors and types of classes.
Challenges and questions
The process of creating a better system still faces many challenges, as speakers at the meeting in Washington made clear. Emily Miller, associate vice president for policy at the AAU, said that many universities were having a difficult time integrating a new approach to evaluating teaching into a rewards system that favors research and that often counts teaching-associated work as service.
“We need to think about how we recognize the value of teaching,” Miller said.
She also summarized questions that had arisen during discussions at the meeting:
- What is good teaching?
- What elements of teaching do we want to evaluate?
- Do we want a process that helps instructors improve or one that simply evaluates them annually?
- What are the useful and appropriate measures?
- What does it mean to talk about parallels between teaching and research?
- How can we situate the conversation about the evaluation of teaching in the larger context of institutional change and university missions?
Noah Finkelstein, a University of Colorado physics professor who is a principal investigator on the TEval grant, brought up additional questions:
- How do we frame teaching excellence within the context of diversity, equity and inclusion?
- How can we create stronger communities around teaching?
- How do we balance institutional and individual needs?
- How do we reward institutions who improve teaching?
- When will AAU membership be contingent on teaching excellence?
Moving the process forward
Instructors at KU, CU and UMass are already grappling with many of the questions that Miller and Finkelstein raised.
At KU, a group will meet on Friday to talk about the work they have done in such areas as identifying the elements of good teaching; gathering evidence in support of high-quality teaching practices; developing new approaches to peer evaluation for faculty and graduate teaching assistants; providing guidance on instructor reflection and assessment; and making the evaluation process more inclusive. There have also been discussions among administrators and Faculty Senate on ways to integrate a new approach into the KU rewards structure. Considerable work remains, but a shift has been set in motion.
KU faculty and staff share insights on teaching
Several KU faculty members have recently published articles about their inquiry into teaching. Their articles are well worth the time to read. Among them:
- Patterns in curricula. Josh Potter, the documenting learning specialist at CTE, writes in Change magazine about a model he has created for showing how students move through classes in a curriculum.
- Physics. Sarah LeGresley Rush, Jennifer Delgado, Chris Bruner, Michael Murray, and Chris Fischer write about their work in rethinking introductory physics. Their paper, published in Physical Review Physics Education Research, was also featured in the online magazine of the American Physical Society.
- Journalism. Carol Holstead, associate professor of journalism and mass communications, writes about the importance of learning students’ names. Her article appeared in The Chronicle of Higher Education.
- Music therapy. Abbey Dvorak, associate professor of music therapy, writes in the Journal of Music Therapy about using a research assignment that involves an entire class pursuing a single question. She also explains the approach in a video.
- History. Tony Rosenthal, professor of history, writes in The Journal of Urban History about an interdisciplinary journey he took in creating assignments and materials for an undergraduate history course called Sin Cities.
Briefly …
- Writing in EdSurge, Bryan Alexander says that “video is now covering a lot of ground, from faculty-generated instructional content to student-generated works, videoconferencing and the possibility of automated videobots.” The headline goes beyond anything in the article, but it nonetheless raises an interesting thought: “Video assignments are the new term paper.”
- The Society for Human Resource Management writes about a trend it calls “microinternships,” which mirror the work of freelancers. Microinternships involve projects of 5 to 20 hours that the educational technology company Parker Dewey posts on a website. Students bid on the work, and Parker Dewey takes a percentage of the compensation. The company says it is working with 150 colleges and universities on the microinternship project.
- Writing in The Chronicle of Higher Education, Aaron Hanlan argues that by relying on a growing number of contingent, “disposable” instructors, “institutions of higher education today operate as if they have no future.” In following this approach, tenured faculty and administrators “are guaranteeing the obsolescence of their own institutions and the eventual erasure of their own careers and legacies,” he argues.
- EAB writes about the importance of reaching out to students personally, saying that email with a personal, supportive tone can be like a lifeline to struggling students.
Peer learning expands as instructors remake courses
Watching David Johnson’s class in digital logic design is a bit like watching synchronized swimming.
After a few minutes of announcements, Johnson and half a dozen GTAs and undergraduate teaching fellows fan out across an Eaton Hall auditorium as 60 or so students begin to work on problems that Johnson has assigned.
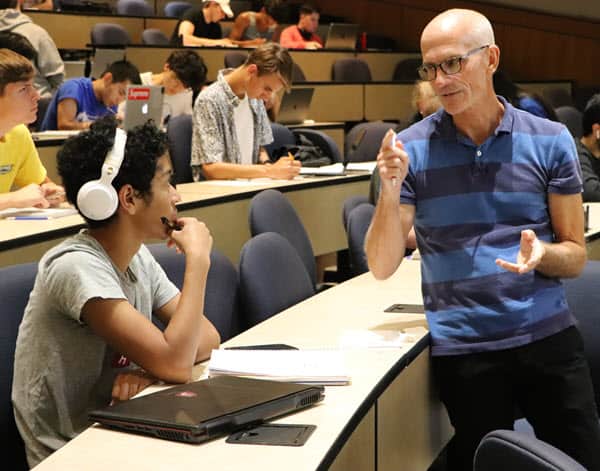

A hand goes up on one side of the room. Johnson approaches, and students around him listen intently as he asks questions and quietly offers advice. Across the aisle, a group of four young men confers about the problem, looking things up on laptops, writing down notes by hand, erasing, writing again, and sharing ideas. A few rows ahead, two young women point at the problem on the screen at the front of the room. They confer, take notes, and confer more. Across the room, hands go up and, one by one, the class assistants approach, offer their help and then search for more raised hands.
“We’re always busy helping someone,” Johnson said.
Similar scenes have increasingly played out across the university – and across the country – as a growing number of instructors, primarily in STEM fields, have hired undergraduate teaching assistants to work in their classes. The undergrad TAs are just one example of how colleges and universities have elevated the importance of peer learning as part of their efforts to retain students and to help them move toward graduation.
Many educational roles
At KU, those efforts extend into many areas. First-Year Experience, honors, pharmacy and business are among the programs that use peer mentors. The Undergraduate Advising Office has a team of peer advisors who, among other things, help students navigate choices of classes and majors, and help them find campus resources. As anxiety and depression have increased among students, Counseling and Psychological Services has created a peer educator program to work with students on mental health.
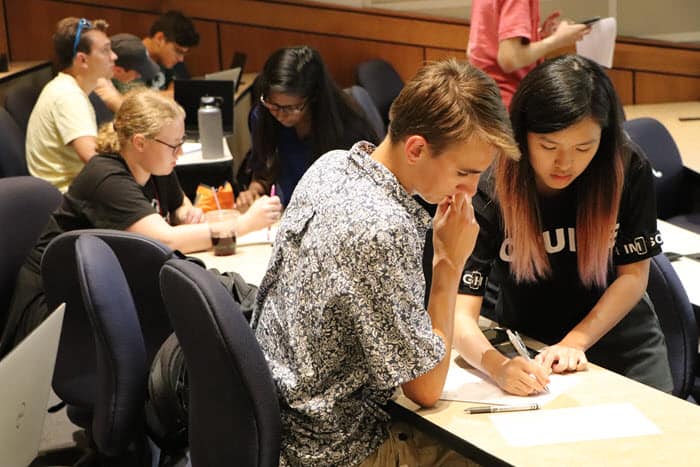

The university’s Supplemental Instruction program is also growing and now has peer leaders working with two dozen courses. Those peer leaders have successfully completed the course they are helping with. They lead sessions in which students review course material, prepare for exams, work on study skills, and offer support to one another throughout a semester. That approach, which started at the University of Missouri-Kansas City, has been found to improve grades, retention rates and, ultimately, graduation rates.
Peers have always played a role in learning, and they have long been involved in writing programs, tutoring and review sessions. The use of large numbers of undergraduate assistants in classes is relatively new, though, and is tied to a growing use of flipped classes, active learning, and in-class problem-solving. Over the past five years or so, KU instructors in such fields as geology, biology, chemistry, physics, and engineering have hired undergraduate assistants to work in their largest classes. Those assistants do such things as monitor online discussion boards, help with labs, proctor exams, and hold office hours. A pre-semester training program was started two years ago for undergraduate assistants in STEM courses, allowing the assistants and instructors to gain a better understanding of how to work together.
Undergraduate assistants have been crucial in transforming large lecture courses into hubs of active learning. Coordinating with instructors and graduate teaching assistants, they monitor groups or sections of a classroom, answer questions, offer praise, and through their interactions with students, make large courses more personal. Like students who lead Supplemental Instruction sessions, the undergraduate assistants in large classes have recently taken the course, so they understand the flow of the class, the course material, and the areas where students are most likely to struggle.
As they help their peers, they hone their own understanding of course material, improve their communication skills, and gain experience working with groups of people. That deeper understanding helps prepare them for upper-level classes as well as medical school exams, internships and graduate school. Most rely on the money they earn to help pay their college bills. Nearly all report a sense of satisfaction from the experience.
“When you see someone finally get it, it’s really cool,” one undergraduate assistant said at a recent training session.

Zero lecture time
Johnson has used graduate teaching assistants, Supplemental Instruction assistants, and undergraduate teaching fellows (as the assistants are known in engineering) to make dramatic changes in his classes. With the help of Molly McVey, a post-doctoral teaching fellow in engineering, Johnson flipped a course in which he was lecturing about half of class time. They created online materials that helped students prepare for in-class problem-solving and hired undergraduate fellows to help in the classroom. When the flipped version debuted last year, lecture time had dropped to nearly zero.
“The only time they really hear me speak is if I have an announcement, usually to remind them of a test,” Johnson said.
Johnson first tried the flipped approach during a summer computer science camp for high school students, and he was surprised by how much more students learned. So he began to transform EECS 140, which he described as a gateway course required of all students in electrical engineering. He received a course transformation grant from the Center for Teaching Excellence and worked with course designers and video specialists at the Center for Online and Distance Learning to create online materials. He had the undergraduate assistants create the in-class problems, which he described as “nearly perfect” because they require considerable thought but can still be completed during class time.
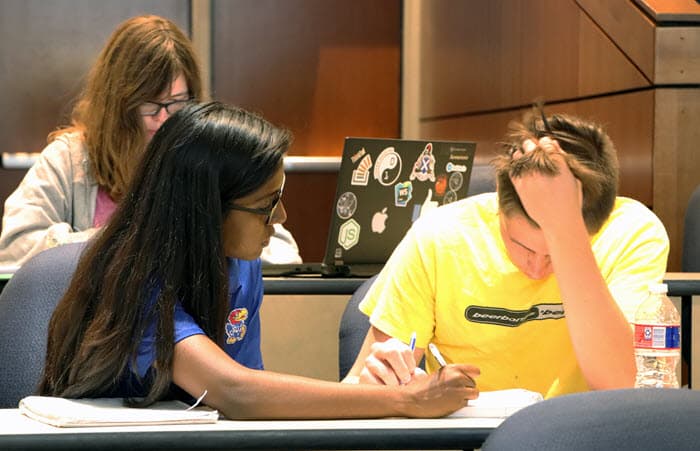

During the first week, students aren’t sure what to make of the hands-on approach, but that hesitancy quickly disappears as they adapt to the in-class problem-solving.
“The first class they were just sitting there waiting,” Johnson said. “I explained to them again that they could start working. By the third or fourth class, they were already asking questions even before the class started.”
The questions continue throughout the class period, and Johnson and the student assistants are constantly on the move. The constant interaction has helped Johnson better connect to the class.
“When I walk around and talk to students, I really understand what they don’t understand,” Johnson said. “That really helps me do a better job.”
Students are free to leave class once they complete the day’s problems, but many stay for the entire period. Some who finish early work on the next online module, knowing they can get help if they have questions. Others like to stay and help their peers.
Improved learning and a sense of satisfaction
Learning has improved significantly in many areas of the class, and the number of students who drop or fail has fallen. The approach isn’t perfect. Johnson said there was a dip in some areas on the last of the four exams he gives. By the end of the semester, though, many students know that their grades won’t change much regardless of how they do on the last exam, so they don’t approach that exam with the same seriousness they do earlier work, Johnson said.
During class, though, the students are focused and engaged. A hand goes up at the back. An undergraduate teaching fellow kneels, listens and offers advice. A hand goes up in front, in the center, on the far side of the room. Johnson moves from table to table, student to student.
“Students always think it’s easy for an instructor to do that,” Johnson said. “For me, it’s a lot harder to go around and explain something to someone who doesn’t understand some things than it is to just stand up there and flap away and hope they understand. It takes a lot more energy out of me, but I feel much better at the end of class when I think, ‘Wow, I really did teach somebody something.’ ”
Moving higher education from storied past to innovative future

We know the story well. We helped write it, after all.
As instructors and students and administrators, we have lived the story of modern higher education. And yet, despite the familiarity of that story – or perhaps because of it – we continue to struggle with its meaning and direction.
Ann Austin, an education professor and administrator at Michigan State, told participants at KU’s annual Teaching Summit last week that that struggle is not only natural; it is also crucial as colleges and universities adapt to a landscape that has changed dramatically over the past 20 years and is poised to change even more dramatically in the next 20.
In her Summit keynote address, Austin moved among the past, present and future as she highlighted the challenges and opportunities that rapid societal changes are posing to colleges and universities. She also challenged faculty members and administrators to think philosophically and creatively about the way they teach, interact and plan.
“What kind of vision do we have in the back of our minds as we go about our day-to-day work?” Austin asked.
“What is our vision for where our learners are going, and what is our vision for the role we play in their lives?”
That vision, after all, guides us in conscious and unconscious ways, and is crucial for the success of the university. We are doing many good things, she said, but we need to be more creative in working with students, curricula and our approach to learning.
‘This noble profession’
Austin maintained an upbeat tone as she made a case that colleges and universities must change to keep pace with society. Universities are exemplars of society, places to share ideas, to advance knowledge and to debate with respect, she said. She evoked the symbolism of KU’s campus on a hill as an indication that it is “involved in something important,” or what she called “this noble profession.”

Even so, those of us who teach and work and learn and lead at universities must push our institutions to adapt and evolve. We have welcomed an increasingly diverse population of students, Austin said, and we must find better ways to support those students. Right now, she said, there’s a mismatch between social needs and educational practices and outcomes. (There is also a growing political rift over the direction of higher education.) We are doing much good, she said, but we need to do more.
“How do we create environments for the success of all?” Austin asked.
She pointed to large gateway classes as an example of where universities have fallen short. Those courses can guide students toward many types of careers – or prevent them from pursuing those careers. Nationally, half of students in those courses fail, she said, and women and students of color encounter the biggest hurdles. By embracing evidence-based teaching practices and taking a more inclusive approach to teaching and learning, though, we can lower the barriers to success.
“We know that if we change the way we go about our teaching, if we think about what will support this diversity of learners, we can pretty much get rid of that gap,” she said, citing years of research about active and engaged learning.
‘Generosity of thinking’ and other any areas of potential
Gateway courses are just one area where there is a mismatch between social needs and educational practices and outcomes, she said. Another involves soft skills, or what Austin calls “human skills”: things like communicating well; discerning between accurate and inaccurate information; understanding the context of problems and actions; engaging in teamwork and collaboration; and approaching work with integrity and ethical standards.

She also singled out something she called “generosity of thinking,” or the ability to work with people different from yourself and to seek out those complementary perspectives on projects at work and in communities.
“We really need to cultivate that even more than perhaps we do,” Austin said.
Austin drew upon her work as co-chair of the Roundtable on Systemic Change in Undergraduate STEM Education for the National Academies of Science, Engineering and Medicine. That group has highlighted the importance of a vibrant educational system and a well-educated citizenry that can join conversations on the challenges facing society. It has also focused on the needs of a changing workforce.
We know that jobs that are common today won’t exist in the future, Austin said. And in 10 or 20 years, “there will be opportunities for work that we can’t even imagine right now.”
“How do we prepare our students for this kind of world?” she asked.
What can we do?
I’ve written before about Austin, who cofounded the Center for Integration of Research, Teaching, and Learning. Her work in organizational change has influenced some of the approaches we take at CTE, and she is a partner on a National Science Foundation grant on creating a more nuanced approach to evaluating teaching. She has worked with many KU faculty members on that project, which is known as Benchmarks for Teaching Effectiveness at KU. The multi-university project is known as TEval.
Austin provides broad insight and thought-provoking questions to everything she does, and the Summit was no exception. She also offered several concrete steps that participants could take to improve their courses, their departments and the learning environments for their students:

- Embrace high-impact practices. These include things like service learning, internships, writing-intensive courses, and learning communities. These and other practices “link the knowing with the doing,” Austin said, and create a more equitable learning environment.
- “Become more fluent in how learning happens.” Research into learning and higher education continually provides new insights, Austin said, urging participants to consider ways of applying that research in their disciplines. CTE programs and materials can help instructors do that without spending hours combing through journals.
- Focus on learning, not seat time. Our courses are organized by credit hours, a system that originated in the 19th century and focused on the amount of time instructors delivered information to students. That system is outmoded, especially for online courses, but we can still work within it, Austin said, by emphasizing learning and using effective means of assessing learning.
- Seek out new ways to reach students. This might involve using technology, taking an innovative approach in face-to-face or online courses or curricula, or using new types of physical classrooms. Austin emphasized the importance of flexibility and creativity in helping students learn. Organize curricula in new ways and look for new pathways that better fit today’s students. She said that included not just degrees but ways for people to move in and out of higher education to refresh skills and share their expertise.
- Cultivate new partnerships. Communities inside and outside the university help us draw on new perspectives, learn from one another, and create new learning opportunities for our students and our colleagues. These partnerships can also provide opportunities for developing and promoting leadership skills that universities need if they hope to innovate.
Even as she pushed audience members to take action, she urged them to draw on the many good things already happening at universities.
“I’m not in any way suggesting that we just jettison what we’re doing,” Austin said. “We do so much that is so good.”
Rather, she suggested committing to effective practices and ask “what is this changing world suggesting that we might do differently?”
Doing so helps us move from story – a beacon on a hill in a volatile, changing world – to action.
“That’s the story we are part of,” Austin said. “We need to think not only in a philosophical way – that’s part of the story – but in a real practical way. What do we do in our departments, in our programs and in the university to actually let us make the best contributions to our learners and to society?”
A cloudy day with lots of sunshine

The Summit took place on the same day that hundreds of students moved in to KU’s residence halls. Chancellor Doug Girod, dressed in khaki slacks and a blue KU polo shirt, said at the beginning of the Summit that he always looked forward to helping with the move-in and talking with students and their families.
The day was cloudy, and the sky threatened rain, but school had yet to start and a shiny eagerness and a positive energy permeated the campus.
“This is one of the few days of the year when everybody smiles,” Girod said.
Doug Ward is the associate director of the Center for Teaching Excellence and an associate professor of journalism. You can follow him on Twitter @kuediting.
Using data to better understand student ‘grade surprise’
A colleague’s daughter recently finished her first year of college. In high school, he said, she had never really had to study to get good grades. In college, though, she had to adjust her study habits and her thinking after her early grades dipped below the A’s and B’s she had routinely – and easily – received.
That sort of dip in grades is common among traditional freshmen as they learn to live away from home for the first time, deal with the liberation and temptations of personal independence, and try to make sense of the academic expectations of college. How they deal with that jolt can affect everything from their choice of majors to their ability to stay in college.
Jennifer Meta Robinson, an anthropology professor at Indiana University-Bloomington, has been studying this phenomenon, which she calls “grade surprise.” Students usually have a good sense of the grades they will receive on assignments or exams, or in a class. When that expectation doesn’t match reality, though, they experience grade surprise.
Robinson explained her research

to the steering committee of the Bay View Alliance earlier this month in Bloomington, Indiana. Both Indiana and KU are members of the Bay View Alliance, a consortium of 10 research-intensive universities that are working to elevate teaching and improve learning among students. Robinson and colleagues in chemistry, computer science and informatics recently received a mini-grant from the Association of American Universities to continue their work of surveying students and analyzing university data to try to find questions they have about grade surprise among students:
- How does grade surprise affect retention in various majors?
- Does the power of grade surprise grow as students move through additional classes?
- What approaches help students recover when they encounter grade surprise?
Robinson’s hypothesis is that grade surprise impedes student progress but can be mitigated. When students are overconfident, she said, failure is more painful than when they have low expectations about their grades. “Surprise creates pain,” Robinson said. She is also looking at the flip side of that: whether there is positive grade surprise. “There’s a human tendency to rewrite the past,” she said. “We mitigate our pain by retelling our story in a way that makes it less surprising.” For instance, students might tell themselves that a low grade was the instructor’s fault or that people like them just don’t do well with this type of material or in these types of classes. That type of thinking can easily push students out of classes or majors. Interestingly, few students seem to blame instructors when grades come in lower than expected. “We were surprised at how few students said, ‘The teacher had it in for me,’” Robinson said. “Or, ‘This was out of left field. I studied this other thing and it wasn’t on the test.’ There was very little of that. It really was about more about what I can do, what I practice, where I can spend more time. The locus of control was within.”
Disparities in distribution and reaction
Grade surprise isn’t equally distributed, Robinson said. Underrepresented minority students and first-generation students are more likely to be surprised by their grades. And women feel more disappointment when they receive lower grades.
Robinson and her colleagues have been sharing context about grades to try to ease some of the pain of grade surprise. For instance, in computer science and informatics classes at Indiana, women generally receive higher grades than men. In chemistry, women and men receive similar grades, although all receive lower grades than they did in high school.
“So women may feel that more, that disappointment in themselves, that setback of, ‘Oh, maybe I don’t belong,’” Robinson said. “But that’s where we could say to them that they may be processing this differently but the GPA facts of it are that they are doing the same.”
An analysis of data at Indiana shows that many students bounce back after the shock of an initial grade. They expect an A, receive a C but then eventually get an A in the course. Robinson and her colleagues want to better understand what students do to recover. They are also looking at the mindset of students who think they did poorly on, say, a midterm exam but actually did well. What happens if they enroll for the subsequent semester before they know their grade?
“What is that little detour through the course?” she asked. “How long does that hang in the air that you think you’ve bombed but you get that assignment back and got that A after all?”
A move toward wider use of data
Robinson describes the grade surprise project as one of many that “connect classes to the potential of big data.” Indiana has an ambitious program in helping faculty members combine university demographic data with data about student performance in classes. That combination is often referred to as learning analytics. The Indiana program, known as Learning Analytics Fellows, has led to more than 50 projects since it started in 2015. It is run through a recently created Center for Learning Analytics and Student Success.
We have been working on a similar project at KU, though at a smaller scale. An AAU mini-grant through the Center for Teaching Excellence has allowed several STEM departments to use university data to learn more about their students and about the paths they take through various curricula. The recently created Office of Analytics and Institutional Research (formerly the Office of Institutional Research and Planning) has continued the momentum around wider application of university data. One of its divisions focuses on academic data analytics and is looking at ways of making more data available to faculty members.
These types of data project allow instructors and departments to ask new questions about curricula, with an eye toward improving student retention and graduation rates. As Robinson explained in her talk at Indiana, this use of data is driving culture change as universities find ways to scale learning analytics even as they explore the potential of data in education. Robinson emphasized the importance of providing context for data and of applying “interpretive muscle” to tease out insights.
“These are drivers for change at all of our universities,” she said.