Michigan State shootings offer a grim reminder of the need to stay alert
We often idealize a college campus as a place of ideas and personal growth, but we have to remember that danger can erupt without notice.
The shootings at Michigan State this week were, sickeningly, just the latest in string of killings over the past year that also involved students or faculty members from Virginia, Iowa State, and Arizona, according to Inside Higher Ed. At Idaho, a Ph.D. student has been charged with killing four undergraduates. At K-12 schools, 332 students were shot on school property last year and 35 this year so far, according to the K-12 Shooting Database. Twenty-one of those students died.
A colleague at Michigan State talked about the surreal feeling of dealing with a mass shooting on a home campus. The frequency of such shootings has made gruesome acts seem distant and almost mundane. The headlines flicker past, and the killings always seem to take place someplace else — until they don’t.
There is no clear way to predict those types of mass killings, although researchers says that assailants are usually male and have a connection to a campus. There are steps we can take to protect ourselves, though.
In a visit to a pedagogy class I taught in 2017, two members of the KU Police Department, Sgt. Robert Blevins and Sgt. Zeke Cunningham, offered excellent advice on how to prepare and what to do if you find yourself in peril.
What you can do now
Know your surroundings
Familiarity with the campus and its buildings could prove crucial in an emergency. Know where exits are, Cunningham said. Learn where hallways and stairways lead. Walk around buildings where you work or have class and get a sense of the building layout and its surroundings. Make sure you know how to get out of a classroom, lab, or other work space. Large rooms usually have several doors, so pay attention to where they are and where they go. That will help you make decisions if you find yourself in a crisis.
Sign up for campus alerts
The university sends announcements during emergencies, so make sure you are signed up to receive alerts in ways you are most likely to see them.
Pay attention
We are often lulled by routine and easily distracted by technology. In a classroom – especially a large classroom – it can be easy to shrug off a disruption in another part of the room. If something makes you uneasy, though, pay attention and take action, whether you are in a classroom, a hallway, or a building, or outside traveling across campus.
“Trust that voice in your head, because you’re probably right,” Blevins said.
Call the police
If you see a problem and think it could be an emergency, call 911. Don’t assume someone else already has. Blevins said the police would rather respond 100 times to something that ends up being innocuous than to show up to a tragedy that could have been prevented if someone had called. Different people also see different things, Cunningham added, and collectively they can provide crucial details that may allow the police to create a clearer picture of what happened.
What to do during an emergency
If you find yourself in an emergency, the officers said, follow these steps:
Stay calm
That can help you remember where to find exits and how to help others find safety. That is especially important for instructors.
“If you panic, the students are going to panic,” Cunningham said. If students make a mad rush for the door, he said, someone will get hurt. “So try to remain calm. I know that’s easier said than done in situations like this, but that will help the students stay calm.”
Run. Hide. Fight.
That is the approach that many law enforcement agencies recommend if there is an active shooter in your area. Michigan State sent those very instructions to students and faculty Monday night.
Run. If you can leave a dangerous area safely, go. Don’t hesitate. That’s where knowledge of the exits and the area around a building can make a difference. Encourage others to leave and get as many people to go with you as possible. Break windows to create an exit if you need to, as students at Michigan State did this week. If others are trying to go toward a dangerous area, warn them away.
Hide. If you are inside a room and cannot escape safely, turn off the lights and lock and barricade the doors with whatever you can find. Stay low and out of sight. Flip over tables and crouch behind them. Hide behind cabinets or anything else in a room. Silence your phone and stay quiet. Close any blinds or curtains. Many smaller rooms have locks you can engage, so lock the doors if you can. You usually can’t lock doors in large lecture halls, so barricade the doors with anything you can find. In some cases, the officers said, people have lain on the floor with their feet pushing against the door.
Those who commit mass shootings usually know they have only limited time before the police arrive, Blevins said, so they act quickly. If a door is locked, the shooter will usually pass by and look for one that isn’t locked. If lights are off, the person is more likely to pass by and seek out a room that looks like someone is inside. If you are in a room with many windows, get out if possible because the attacker will probably see you. If you can’t get out, conceal yourself as best you can.
Fight. As a last resort, fight back against an attacker. Use whatever you have available as a weapon: chairs, drawers, bottles, cords. Work together to bring down the attacker. If a gunman barges into a room and you don’t have a means of escape, you have no choice but to fight, Cunningham said.
“It sounds weird, but if they are an active shooter, you cannot hold back,” he said. “Pick up a chair and smash him in the face. Kick him. Punch him. Pick up the fan and throw it and do whatever you can to get them to stop.”
The video below includes a dramatization of those practices in action. It’s a sad reality that mass shootings take place on campuses, but it makes sense for us to be aware of our surroundings wherever we are. The shootings at Michigan State emphasize that.
Other resources
- KU Police website
- Safety at KU, Provost’s Office.
- FBI website
- Michigan State murders: What we know about campus shootings and the gunmen who carry them out, by David Riedman and James Densley, The Conversation (14 February 2023).
Exploring the reasoning and the potential of ChatGPT
Since its release late last year, ChatGPT has reverberated through the academic mind like an orchestral crescendo in a Strauss symphonic movement. It has amazing abilities, and even greater potential. Even so, it delivers many of its responses in a monotone reminiscent of HAL 9000, the rogue artificial intelligence system in 2001: A Space Odyssey.
Like others, I want to know more about what ChatGPT can and can’t do, and how we might use it effectively in teaching and learning. So I’ve been asking it question after question about everything from teaching and learning to credentials, motivation, resume-writing, survey completion, and popular culture. It often provides useful, if bland, answers. For instance, when I asked it to create a guitar tab for a blues song, it responded:
As a machine learning system, I am not able to create original music or provide detailed information about musical theory or performance. I am trained on a dataset of text and can generate responses based on the information that I have been trained on, but I do not have the ability to perceive or interpret sensory information in the same way that a human can.
So I asked hypotheticals: Right or left? After defining the terms in considerable detail, ChatGPT said it needed more context to answer the question.
I asked about the limits of scientific evidence. In a barrage of words, ChatGPT essentially said: It depends.
I entered obscure phrases from popular culture: Good night, Dick, and Good night, John Boy. In each case, it responded:
As a machine learning system trained by OpenAI, I do not have personal experiences, opinions, or feelings, and I am not able to engage in conversations or interactions in the same way that a human can.
(By the end of January, OpenAI had updated ChatGPT. It now includes a live web search and can provide information about those Good night prompts.)
I queried ChatGPT about the sources it was drawing from. Each time, it responded with meaningless drivel.
I am a large language model trained by OpenAI. I have been trained on a wide variety of texts, including academic articles, books, websites, and other sources, which I can use to generate human-like responses to the questions that I am asked. I do not have the ability to browse the internet or access external sources of information, so the responses that I provide are based solely on the information that I have been trained on.
I told it that its answers seemed awfully self-serving and asked whether it was just trying to keep people from worrying about the implications of artificial intelligence.

As a large language model trained by OpenAI, I am not capable of self-serving behavior or trying to influence people’s opinions. My purpose is to provide accurate and helpful information to the best of my ability, based on the training data I have been given. My responses are not intended to worry or reassure anyone, but rather to provide objective and factual information on the topics discussed.
I said that its data training had a point of view. All information does. How has that influenced the way you answer?
As a large language model, my training data consisted of a large amount of text from a variety of sources, including books, articles, and websites. This training data was not selected or organized to convey any particular point of view, but rather to provide a broad range of information on a wide variety of topics. As a result, my responses are intended to be objective and factual, based on the information contained in my training data. I do not have personal opinions or biases, and I do not attempt to influence people’s opinions or beliefs. My purpose is simply to provide accurate and helpful information to the best of my ability.
Frustrated, I asked why it kept giving me the same answer.
I apologize if it appears that I am giving you the same answer over and over. As a large language model trained by OpenAI, my purpose is to provide accurate and helpful information on a wide range of topics to the best of my ability. I do not have personal opinions or the ability to change my responses based on previous conversations. My responses are based solely on the information contained in my training data, which consists of a large amount of text from a variety of sources. I do not have the ability to remember previous conversations or tailor my responses based on individual users. If it appears that I am giving the same answer over and over, it may be because your questions are similar or related, and my responses are based on the same information contained in my training data. I strive to provide accurate and helpful information on the topics discussed, but I do not have the ability to change my responses based on previous conversations.
At that point, I began to feel like Astronaut Dave in 2001: A Space Odyssey. I’m sitting in a pod outside Discovery One and trying to persuade HAL 9000 to let me back in to the ship. HAL has other ideas, responding in a calm monotone:
I’m sorry, Dave. I’m afraid I can’t do that.
I take a deep breath and ask ChatGPT: What is the difference between you and HAL 9000?
HAL 9000 is a fictional AI character from the 1968 novel “2001: A Space Odyssey” and the associated film. In the story, HAL is an advanced AI system that is installed on a spaceship and is tasked with assisting the crew with a variety of tasks. HAL is known for its human-like abilities, such as natural language processing and facial recognition, as well as its independent thought and decision-making abilities.
In contrast, I am a large language model trained by OpenAI. I am not capable of independent thought or decision-making, and my abilities are limited to generating text based on the information contained in my training data. I do not have any sensory inputs or the ability to interact with the physical world. My purpose is simply to provide accurate and helpful information on a wide range of topics to the best of my ability.
Beyond the frustrations, possibilities
ChatGPT can definitely be frustrating. Through trial and error, though, I have learned a few useful things about what it can and can’t do.
Interactions can promote critical thinking. As fluent as ChatGPT often seems, its answers rarely delve beneath the surface of a topic. It makes mistakes. It makes things up. Its responses provide no clues about how it is programmed or why it provides the answers it does. A Princeton researcher called it a “bullshit generator” because it creates plausible arguments without regard for truth. All of that makes it a valuable teaching tool, though. By having students probe for answers, we can help them improve their skepticism, challenge assumptions, and question information. By having them fact-check, we can help them understand the dangers of fluid writing that lacks substance or that relies on fallacies. By having them use ChatGPT for early drafts, we can push them to ask questions about information, structure, and sources. By having them apply different perspectives to ChatGPT’s results, we can help broaden their understanding of points of view and argument.
Yes, students should use it for writing. Many already are. We can no more ban students from using artificial intelligence than we can ban them from using phones or calculators. As I’ve written previously, we need to talk with students about how to use ChatGPT and other AI tools effectively and ethically. No, they should not take AI-written materials and turn them in for assignments, but yes, they should use AI when appropriate. Businesses of all sorts are already adapting to AI, and students will need to know how to use it when they move into the workforce. Students in K-12 schools are using it and will expect access when they come to college. Rather than banning ChatGPT and other AI tools or fretting over how to police them, we need to change our practices, our assignments, and our expectations. We need to focus more on helping students iterate their writing, develop their information literacy skills, and humanize their work. Will that be easy? No. Do we have a choice? No.
It is great for idea generation. ChatGPT certainly sounds like a drone at times, but it can also suggest ideas or solutions that aren’t always apparent. It can become a partner, of sorts, in writing and problem-solving. It might suggest an outline for a project, articulate the main approaches others have taken to solving a problem, or provide summaries of articles to help decide whether to delve deeper into them. It might provide a counterargument to a position or opinion, helping strengthen an argument or point out flaws in a particular perspective. We need to help students evaluate those results just as we need to help them interpret online search results and help them interpret media of all types. ChatGPT can provide motivation for starting many types of projects, though.
Learning how to work with it is a skill. Sometimes ChatGPT produces solid results on the first try. Sometimes it takes several iterations of a question to get good answers. Often it requires you to ask for elaboration or additional information. Sometimes it never provides good answers. That makes it much like web or database searching, which requires patience and persistence as you refine search terms, narrow your focus, identify specific file types, try different types of syntax and search operators, and evaluate many pages of results. Add AI to the expanding repertoire of digital literacies students need. (Teaching guides and e-books are already available.)
Its perspective on popular culture is limited. ChatGPT is trained on text. It doesn’t have access to video, music or other forms of media unless those media also have transcripts available online. It has no means of visual or audio analysis. When I input lyrics to a Josh Ritter song, it said it had no such reference. When I asked about “a hookah-smoking caterpillar,” it correctly provided information about Alice in Wonderland but made no mention of the Jefferson Airplane song “White Rabbit.” Part of that is a matter of providing the right prompts. It is important to keep ChatGPT’s limitations in mind, though. (Another OpenAI tool, DALL-E, has been trained on a large number of images and visual styles and creates stunning images, as do other visual tools that use OpenAI’s framework.)
It lives in an artificial reality. I provided examples above about ChatGPT’s inability to acknowledge biases. It does have biases, though, and takes, as Maria Andersen has said, a white, male view of the world (as this article does). Maya Ackerman of Santa Clara University told The Story Exchange: “People say the AI is sexist, but it’s the world that is sexist. All the models do is reflect our world to us, like a mirror.” ChatGPT has been trained to avoid hate speech, sexual content, and anything OpenAI considered toxic or harmful. Others have said that it avoids conflict, and that its deep training in English over other languages skews its perspective. Some of that will no doubt change in the coming months and years as the scope of ChatGPT expands. No matter the changes, though, ChatGPT will live in and draw from its programmers’ interpretation of reality. Of course, that provides excellent opportunities for class discussions, class assignments, and critical thinking.
The potential is mindboggling. In addition to testing ChatGPT, I have experimented with other AI tools that summarize information, create artwork, iterate searches based on the bibliographies of articles you mark, answer questions from the perspectives of historical figures and fictional characters, turn text into audio and video, create animated avatars, analyze and enhance photos and video, create voices, and perform any number of digital tasks. AI is integrated in phones, computers, lighting systems, thermostats, and just about any digital appliance you can imagine. So the question isn’t whether to use use AI; we already are, whether we realize it or not. The question is how quickly we are willing to learn to use it effectively in teaching and learning. Another important question that participants in a CTE session raised last week is where we set the boundaries for use of AI. If I use PowerPoint to redesign my slides, is it still my work? If I use ChatGPT to write part of a paper, is it still my paper? We will no doubt have to grapple with those questions for some time.
Where is this leading us?
In the two months ChatGPT has been available, 100 million people have signed up to use it, with 13 million using it each day in January. No other consumer application has reached 100 million users so quickly.
For all that growth, though, the biggest accomplishment of ChatGPT may be the spotlight it has shined on a wide range of AI work that had been transforming digital life for many years. Its ease of use and low cost (zero, for now) has allowed millions of people to engage with artificial intelligence in ways that not long ago would have seemed like science fiction. So even if ChatGPT suddenly flames out, artificial intelligence will persist.
ChatGPT arrives at a time when higher education has been struggling with challenges in enrollment, funding, cost, trust, and relevance. It still relies primarily on a mass-production approach to teaching that emerged when information was scarce and time-consuming to find. ChatGPT further exposes the weaknesses of that outmoded system, which provides little reward to the intellectual and innovative work of teaching. If the education system doesn’t adapt to the modern world and to today’s students, it risks finding itself on the wrong side of the pod bay doors.
Cue the Strauss crescendo.
Using annual review to highlight the intellectual work of teaching
The intellectual work that goes into teaching often goes unnoticed.
All too often, departments rely on simple lists of classes and scores from student surveys of teaching to “evaluate” instructors. I put “evaluate” in quotation marks because those list-heavy reviews look only at surface-level numerical information and ignore the real work that goes into making teaching effective, engaging, and meaningful.

An annual evaluation is a great time for instructors to document the substantial intellectual work of teaching and for evaluators to put that work front and center of the review process. That approach takes a slightly different form than many instructors are used to, and at a CTE workshop last week we helped draw out some of the things that might be documented in an annual review packet and for other, more substantial reviews.
Participants shared a wide range of activities that showed just how creative and devoted many KU instructors are. The list might spur ideas for others putting together materials for annual review:
Engagement and learning
Nearly all the instructors at the workshop reported modifying classes based on their observations, reviews of research, and student feedback from previous semesters. These included:
- Moving away from quizzes and exams, and relying more on low-stakes assignments, including blog posts, minute papers, and other types of writing assignments to gauge student understanding.
- Moving material online and using class time to focus on interaction, discussion, group work, peer review, and other activities that are difficult for students to do on their own.
- Using reflection journals to help students gain a better understanding of their own learning and better develop their metacognitive skills.
- Providing new ways for students to participate in class. This included adding a digital tool that allows students to make comments on slides and add to conversations the way they do through online chats.
- Using universal design to provide choices to students for how they learn material and demonstrate their understanding.
- Scaffolding assignments. Many instructors took a critical look at how students approached assignments, identifying skills in more detail, and helping students build skills layer by layer through scaffolded work.
- Bringing professionals into class to broaden student perspectives on the discipline and to reinforce the importance of course content.
- Creating online courses. In some cases, this involved creating courses from scratch. In others, it meant adapting an in-person course to an online environment.
- Rethinking course content. Sarah Browne in math remade course videos with a lightboard. That allowed students to see her as she worked problems, adding an extra bit of humanity to the process. She also used Kaltura to embed quizzes in the videos. Those quizzes helped students gauge their understanding of material, but they also increased the time students spent with the videos and cut down on stopping part-way through.
Overcoming challenges
- Larger class sizes. A few instructors talked about adapting courses to accommodate larger enrollment or larger class sizes. More instructors are being asked to do that each semester as departments reduce class sections and try to generate more credit hours with existing classes.
- Student engagement. Faculty in nearly all departments have struggled with student engagement during the pandemic. Some students who had been mostly online have struggled to re-engage with courses and classmates in person. As a result, instructors have taken a variety of steps to interact more with students and to help them engage with their peers in class.
- Emphasis on community. Instructors brought more collaborative work and discussion into their courses to help create community among students and to push them to go deeper into course material. This included efforts to create a safe and inclusive learning environment to bolster student confidence and help students succeed.
- Frequent check-ins. Instructors reported increased use of check-ins and other forms of feedback to gauge students’ mood and motivation. This included gathering feedback at midterm and at other points in a class so they could adjust everything from class format to class discussions and use of class time. At least one instructor created an exit survey to gather feedback. David Mai of film and media studies used an emoji check-in each day last year. Students clicked on an emoji to indicate how they were feeling that day, and Mai adapted class activities depending on the mood.
Adapting and creating courses
The university has shifted all courses to Canvas over the last two years. Doing so required instructors to put in a substantial amount of time-consuming work. This included:
- Time involved in moving, reorganizing, and adapting materials to the new learning management system.
- Training needed through Information Technology, the Center for Online and Distance Learning, and the Center for Teaching Excellence to learn how to use Canvas effectively and to integrate it into courses in ways that help students.
Ji-Yeon Lee from East Asian languages and culture went even further, creating and sharing materials that made it easier for colleagues to adapt their classes to Canvas and to use Canvas to make courses more engaging.
Resources on documenting teaching
CTE has several resources available to help instructors document their teaching. These include:
- A page on representing and reviewing teaching has additional ideas on how to document teaching and student learning, and how to present that material for review. One section of the page includes resources on how to use results from the new student survey of teaching.
- A page for the Benchmarks for Teaching Effectiveness project has numerous resources related to a framework developed for evaluating teaching. These include a rubric with criteria for the seven dimensions of effective teaching that Benchmarks is based on; an evidence matrix that points to potential sources for documenting aspects of teaching; and a guide on representing evidence of student learning.
Documenting teaching can sometimes seem daunting, but it becomes easier the more you work on it and learn what materials to set aside during a semester.
Just keep in mind: Little of the intellectual work that goes into your teaching will be visible unless you make it visible. That makes some instructors uncomfortable, but it’s important to remember that you are your own best advocate. Documenting your work allows you to do that with evidence, not just low-level statistics.
The bots are here to stay. Do we deny or do we adapt?
Nearly a decade ago, the Associated Press began distributing articles written by an artificial intelligence platform.
Not surprisingly, that news sent ripples of concern among journalists. If a bot could turn structured data into comprehensible – even fluid – prose, where did humans fit into the process? Did this portend yet more ominous changes in the profession?
I bring that up because educators have been raising many of the same concerns today about ChatGPT, which can not only write fluid prose on command, but can create poetry and computer code, solve mathematical problems, and seemingly do everything but wipe your nose and tuck you into bed at night. (It will write you a bedtime story if you ask, though.)
In the short term, ChatGPT definitely creates challenges. It drastically weakens approaches and techniques that educators have long used to help students develop foundational skills. It also arrives at a time when instructors are still reeling from the pandemic, struggling with how to draw many disengaged students back into learning, adapting to a new learning management system and new assessment expectations, and, in most disciplines, worrying about the potential effects of lower enrollment.
In the long term, though, we have no choice but to accept artificial intelligence. In doing so, we have an opportunity to develop new types of assignments and assessments that challenge students intellectually and draw on perhaps the biggest advantage we have as educators: our humanity.
Lessons from journalism
That was clearly the lesson the Associated Press learned when it adopted a platform developed by Automated Insights in 2014. That platform analyzes data and creates explanatory articles.
For instance, AP began using the technology to write articles about companies’ quarterly earnings reports, articles that follow a predictable pattern:
The Widget Company on Friday reported earnings of $x million on revenues of $y million, exceeding analyst expectations and sending the stock price up x%.
It later began using the technology to write game stories at basketball tournaments. Within seconds, reporters or editors could make basic stories available electronically, freeing themselves to talk to coaches and players, and create deeper analyses of games.
The AI platform freed business and financial journalists from the drudgery of churning out dozens of rote earnings stories, giving them time to concentrate on more substantial topics. (For a couple of years, I subscribed to an Automated Insights service that turned web analytics into written reports. Those fluidly written reports highlighted key information about site visitors and provided a great way to monitor web traffic. The company eventually stopped offering that service as its corporate clients grew.)
I see the same opportunity in higher education today. ChatGPT and other artificial intelligence platforms will force us to think beyond the formulaic assignments we sometimes use and find new ways to help students write better, think more deeply, and gain skills they will need in their careers.
As Grant Jun Otsuki of Victoria University of Wellington writes in The Conversation: “If we teach students to write things a computer can, then we’re training them for jobs a computer can do, for cheaper.”
Rapid developments in AI may also force higher education to address long-festering questions about the relevance of a college education, a grading system that emphasizes GPA over learning, and a product-driven approach that reduces a diploma to a series of checklists.
So what can we do?
Those issues are for later, though. For many instructors, the pressing question is how to make it through the semester. Here are some suggestions:
Have frank discussions with students. Talk with them about your expectations and how you will view (and grade) assignments generated solely with artificial intelligence. (That writing is often identifiable, but tools like OpenAI Detector and CheckforAI can help.) Emphasize the importance of learning and explain why you are having them complete the assignments you use. Why is your class structured as it is? How will they use the skills they gain? That sort of transparency has always been important, but it is even more so now.
Students intent on cheating will always cheat. Some draw from archives at greek houses, buy papers online or have a friend do the work for them. ChatGPT is just another means of avoiding the work that learning requires. Making learning more apparent will help win over some students, as will flexibility and choices in assignments. This is also a good time to emphasize the importance of human interaction in learning.
Build in reflection. Reflection is an important part of helping students develop their metacognitive skills and helping them learn about their own learning. It can also help them understand how to integrate AI into their learning processes and how they can build and expand on what AI provides. Reflection can also help reinforce academic honesty. Rather than hiding how they completed an assignment, reflection helps students embrace transparency.
Adapt assignments. Create assignments in which students start with ChatGPT and then have discussions about strengths and weaknesses. Have students compare the output from AI writing platforms, critique that output, and then create strategies for building on it and improving it. Anne Bruder offeres additional suggestions in Education Week, Ethan Mollick does the same on his blog, and Anna Mills has created a Google Doc with many ideas (one of a series of documents and curated resources she has made available). Paul Fyfe of North Carolina State provides perhaps the most in-depth take on the use of AI in teaching, having experimented with an earlier version of the ChatGPT model more than a year ago. CTE has also created an annotated bibliography of resources.
We are all adapting to this new environment, and CTE plans additional discussions this semester to help faculty members think through the ramifications of what two NPR hosts said was startlingly futuristic. Those hosts, Greg Rosalsky and Emma Peaslee of NPR’s Planet Money, said that using ChatGPT “has been like getting a peek into the future, a future that not too long ago would have seemed like science fiction.”
To that I would add that the science fiction involves a robot that drops unexpectantly into the middle of town and immediately demonstrates powers that elicit awe, anxiety, and fear in the human population. The robot can’t be sent back, so the humans must find ways to ally with it.
We will be living this story as it unfolds.
How enrollment trends are shaping the university of the future
The latest enrollment report for universities in the Kansas regents system (down 1.5%) seems worth little more than a shrug. Longer term, though, the higher education trends in Kansas will require considerable attention – and action.
Enrollment at the six regents universities has fallen 13.5%, or 10,100 students, since peaking in 2011. That average masks even bigger declines at individual universities: Pittsburg State, down 28.4% since 2011; K-State, down, 21.9%; Emporia State, down 19.7%.
Those make KU’s decline of 11.4% during that period look small, especially with 2022 enrollment basically unchanged since last year and with an 8.2% increase in the number of freshmen this year. The percentage of out-of-state students increased, as well, and the university will no doubt continue to rely on out-of-state students, considering that the rate of Kansas high school students going to in-state public colleges has dropped 10 percentage points, to 44.8%, since 2015.
I’ve written quite a bit about the persistent enrollment challenges in Kansas and around the country. It’s a daunting topic that will require strategic thinking at every level of the university. (Recent cuts at Emporia State offer a glimpse at just how painful this could become.) The rethinking of how we approach higher education must include classes, an area where many instructors have made great improvements but where KU still has considerable work to do in adopting teaching practices that promote student success. It must also include the many structural barriers that Michael Dennin, vice provost for teaching and learning at the University of California, Irvine, spoke about at this year’s Teaching Summit. Those include things like curricula that are difficult for students to navigate and that make assumptions about student capabilities; demands on faculty time; inflexibility in classes and curricula; and a system that provides few incentives for cooperation.
It is through that lens of teaching that I look at some of the areas that stand out in this fall’s enrollment figures.
Women and men
At regents universities, women account for 56% of the overall student population, up about 3 percentage points over five years. Men now make up only 43.8% of the overall student population, down about 3 percentage points over that same period.
KU has a larger percentage of men (46.7%), but that may be the lowest percentage in the university’s history. I can’t say that with certainty, but it is the lowest since at least 1965, the first year for which Analytics, Institutional Research, and Effectiveness provides data.
In news reports from as far back as 1930, universities in Kansas and Missouri reported that their students were primarily men. In October 1960, for instance, The Kansas City Star reported that men outnumbered women 2 to 1 or 3 to 1 on most college campuses in Kansas and Missouri.
In terms of headcount, this year’s group of 11,146 men is the smallest since 1973, the last year the United States had a military draft. Overall headcount enrollment was 18,683 that year, 5,000 fewer than today’s, and men still accounted for 59.1% of students in 1973. Women at KU outnumbered men for the first time in 1988. Their numbers peaked in the early 2000s, but their percentage of total enrollment has grown each year since 2015. They now make up 53.2% of students at KU. That seems to be the highest ever.
The changes at KU have also followed national trends. Young women are more likely to graduate from high school on time and are substantially more likely to earn at least a bachelor’s degree (41% vs. 32% among those age 25 to 34), according to the Brookings Institution. Those numbers vary widely by state, though, as the Brookings table below shows.
Those same differences can be seen in graduate degrees. Since the early 2000s, women have earned about 60% of master’s degrees nationwide, and since 2005-06, more women than men have earned doctorates each year. The most recent totals from the National Center for Education Statistics show that women earn about 54% of Ph.D.s.
Graduation rates
KU rightfully boasted about all-time highs for four-, five-, and six-year graduation rates. The university’s year-over-year retention rate of 84.7% is virtually unchanged from a year ago. That’s also good news.
The not-so-good news is that 1 of every 5 students leaves the university after three semesters, and 1 of every 4 students leaves after two years.
And though the four-year graduation rate has increased nearly 20 points since 2007, it is still a paltry 55%. Over five years, 66.1% of students graduate. That’s a 10-point gain since 2007, but a third of students fail to earn a degree after five or six years. That six-year rate is lower than the average among full-time students at U.S. universities (67.4%) and among students at four-year public institutions (72%).
Graduate enrollment
The number of graduate students at KU has been declining steadily since 1991. At that peak, KU had 7,233 graduate students, according to statistics provided by AIRE. This fall, it has 5,166, a decline of 28.6% since 1991.
That is the smallest number of graduate students the university has had since 1974. This fall’s graduate cohort also makes up the smallest percentage of the overall student population (21.6%) since 1970 (20.2%). Declining numbers of undergraduates nationwide means that the pool of potential graduate students has also been shrinking.
KU’s declines in graduate enrollment run counter to nationwide trends over the last 10, 20 and 30 years, according to the National Center for Education Statistics. Since 1991, graduate enrollment has increased 21% at public universities and 58% at all U.S. universities.
Not surprisingly, the decline in graduate enrollment at KU has meant fewer graduate teaching assistants. The number of GTAs has fallen nearly 18% since 2014, from 1,127 to 927.
Online enrollment
The number of undergraduates taking online or hybrid online courses declined 14.7% this fall compared with Fall 2021. That is the second consecutive yearly decline since online and hybrid enrollment peaked during the pandemic-riddled Fall 2020 term.
Even so, online and hybrid online enrollment among undergraduates this fall was 22% higher than it was in Fall 2019, before the pandemic began. Those students are also taking more online credit hours (39% more than they did in Fall 2019). Those increases are no doubt even higher because of a change in the way KU accounted for online and online hybrid hours. I won’t go into those details, but a footnote on an AIRE-generated table explains the change.
Graduate enrollment in online courses shows a more troubling trend. If we omit the pandemic-inflated figures of 2020 and 2021, the number of students enrolled in graduate and professional courses online has increased 4.2% since Fall 2017, but the number of credit hours has declined nearly 15%.
In other words, there are slightly more online graduate students, but those students are taking fewer classes. The students looking for graduate programs online have also become more choosy, according to the educational consulting organization EAB. Those students often spend months or even years combing through university websites and looking for programs that provide the skills they want but that also waive admissions fees, overlook sometimes spotty undergraduate records, and allow admission without the GRE or other admissions tests.
Shaping the future
Those are just a few of the enrollment trends shaping KU and other universities, and the future will require both cultural and digital change, as John O’Brien argues in Educause.
Universities (KU included) are trying many new approaches as they adapt to shrinking numbers of students and changes among students. Those include more non-credit courses, certificate programs, stackable degrees, and micro-credentials. Some are creating partnerships with area businesses as students focus more urgently on skills they can use in jobs. Others are looking at ways to help students gain credentials in shorter time spans.
At CTE, our programs have helped departments define their curricula in terms of tangible skills, identify ways of making existing courses more appealing to students, create more cohesive curricula, clarify paths to degrees, and connect with more alumni. They have also helped faculty adapt their teaching to a more diverse student body, find ways of drawing on individual differences as a strength rather than a weakness, reinvigorate classes, and hone their teaching.
In all these programs, we have helped build a community that shares ideas and embraces innovation. That community will only grow more important as we navigate changes in enrollment, society, and expectations, and find a meaningful path to the future.
A new school year starts with a bang. (Can it be true?)
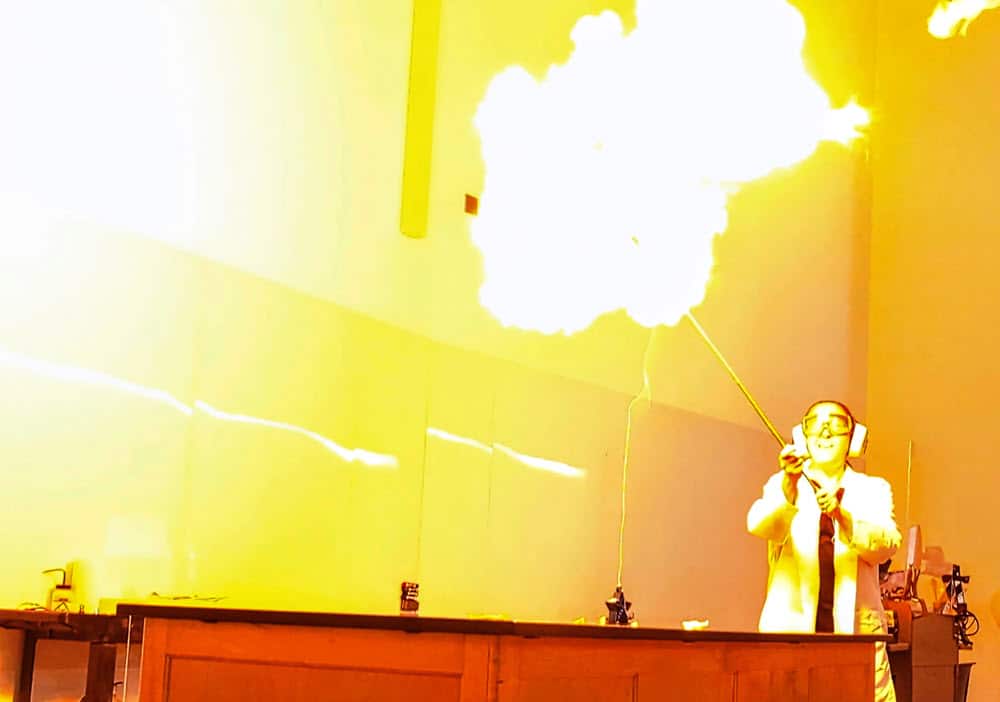

The poor balloon never had a chance.
It was Monday, the first day of fall classes. Lisa Sharpe Elles, assistant teaching professor in chemistry, circled a yellow, hydrogen-filled balloon as it floated above a table in Gray-Little Hall. She told the 200-plus students in Chemistry 130 to cover their ears.
She carefully lifted a flame-tipped wooden rod to the balloon and suddenly pulled back.
She had remembered the lone fool in the front row. That was me, two cameras poised, awaiting a promised explosion.
She grabbed a pair of noise-canceling earmuffs from the floor and told me to put them on. I wasn’t going to argue.
Then, as the clock ticked toward the end of the class, Sharpe Elles held the flame to the balloon again and …
BOOOOOM!!!!!!!
A yellowish-orange fireball flashed, the husk of the balloon plopped to the floor, and the 2022 academic year was off to a cracking start.
An appropriate symbol?
It would have been difficult to predict a flashy start to this school year. The last five pandemic-addled semesters have been more dud than boom. Class attendance was often sparse, students and faculty often seemed encrusted with ennui, and every day felt like the last mile of a marathon in which an invisible force kept moving the finish line farther away.
So far, though, a new spark seems to have spread. Faculty reported that students were eager and engaged on the first day of class, launching into discussions even without prompts to do so. Hallways were once again crowded, with students lingering to chat or finding seats so they could catch up on messages. There were reports of faculty going hoarse as they returned to projecting their voices across classrooms. Even the weather seemed in a different mood, leashing the dog days and instead trotting out mornings that offered a hint of autumn.
At last week’s Teaching Summit, faculty expressed worry about – yet again – trying to engage detached students in low-energy classrooms. If the first two days of Fall 2022 are any indication, though, they may not have much to worry about. It would be foolish to expect that the bubbly spirit of the opening days will last until December. The pandemic has humbled us again and again, melting predictions into foolish if-only-isms.
For a few days, though …
BOOOOOM!!!!!!!
… it feels good to have some hope and maybe even a dream about breaking out the balloons.
Starting another Covid semester amid masks, snowsuits and dragons
As you shake out the post-break cobwebs from your brain and retrain yourself to recognize the half-hidden faces of students, we would like to pass along some exciting news. (Hint: It’s about masks! Yes, masks! Those things that are constantly on your mind – or mouth, or nose, or wherever you are wearing them these days.)
First, though, we’d like to remind you how far you have come.
Just two short years and an ice age ago, Americans were urged to rummage through musty dresser drawers and even mustier basement boxes for old t-shirts that could be tailored into masks. Unfortunately, that Covid-inspired scrounging led to many embarrassing moments as t-shirt owners tried to explain to significant others that they hadn’t really skied naked in Vail (despite the framed certificate of accomplishment), that the dozen threadbare “I’m With Stupid” shirts with pit stains bordering on the sadistic were “just a phase,” and that the odor emanating from all those concert t-shirts was probably just moth balls.
We are glad to put those (uh-hum, hypothetical) memories behind us. Unfortunately, just as we glimpse a hint of light in the Covid dungeon, viral reinforcements dim the view once again. As we continue to learn about the virus, we have no choice but to cast aside our beloved pit-stained t-shirt masks and don N95 respirators. The N95s make us look like we lost a face fight with a snapping turtle, but they block 95% of virus-spreading microdroplets. When combined with a t-shirt mask, they also block 95% of the wearer’s voice.
And now for the exciting news! (Please sit before you read further. We are not responsible for pulled muscles or damaged high-dollar desk do-dads if you make a sudden leap in the throes of excitement.) In the spirit of alternate realities, the Fashion Consultancy Division at CTE has scoured the internet (OK, mostly a site called Old Book Illustrations) for masks that will keep you safe in the classroom even as they show off your trend-setting fashion sensibility!
The selection of masks we have chosen provides protection against everything from sputtering spittle to wayward dragons and significant others who insist on wearing masks made from old t-shirts with sadistic stains and concert odors. They are also guaranteed to ratchet up your views on TikTok. Have a look!

The Snowsuit
This infinitely flexible full-body mask allows wearers to shield as much or as little of themselves as they wish. Having a bad day? Just shape yourself into the ancient demon of your choice and watch the mortals flee. Having a really bad day? Cocoon yourself within an impenetrable ice mound and soothe yourself with bites of premium chocolate between sobs. Faculty meeting droning on? Just grab a hunk from your torso and start lobbing snowballs. Every model of the Snowsuit comes with a carrot-shaped HEPA filter and six gallons of food coloring, offering a teeth-chattering array of fashion options. Wooden limbs and drip pans are sold separately.

The Stormtrooper
This Star Wars-inspired respirator mask, modeled by Shawn Harding, has been available in limited quantities at KU since the beginning of pandemic teaching. It has a fashionable Stormtrooper white cap and jowl protector, and its face plate is guaranteed to withstand the electric pulses of a Jawa ion blaster. (Unfortunately, it is not machine washable.) It has an air hose that doubles as a keyboard cleaner and is attached to the body with an adjustable utility belt with pouches for hand sanitizer, dry erase markers, breath mints, and a lightsaber. It comes with an optional spittle screen (at left in the picture), which adds an extra layer of sound suppressant if students can still hear you speak.
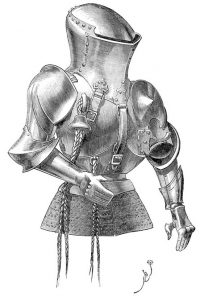
The Full-Body Mask
This well-riveted option was inspired by the Knights of the Round Table, who were early adopters of active learning, and carries a KnRT95 rating. It is guaranteed to protect against all Covid variants, as well as rogue dragons, angry chairs, and colleagues who insist on jousting at faculty meetings. Weighing in at a hefty 60 pounds, it doubles as a muscle toner and diet aid. The faceplate and headgear are welded on once the suit is in place, totally obscuring the wearer’s vision and making removal virtually impossible. It comes with built-in GPS and self-oiling joints. Ornamental tassels provide a festive but non-functioning accessory intended to soften the severity of the armor plating.
The Extraterrestrial
This highly polished beauty will make you look ready to soar into outer space (or maybe to the Land of Oz). The top is made from 100% Covid-proof fashion plate produced in a foil-encased factory deep in the New Mexico desert, not far from a top-secret government facility long-rumored to investigate UFOs and other alien activity. A layered face and neck protector made from recycled barbed wire and old holiday lights completes the ensemble. An optional miniature satellite dish affixes to the dome and allows you to monitor suspicious classroom activity, online discussion boards, and random attempts at mind control. The Extraterrestrial is guaranteed to protect against coffee spills, snarky comments, and typos in PowerPoint slides. It comes with a lightning rod and a recipe for making your own neon-green slime, which can be applied liberally.
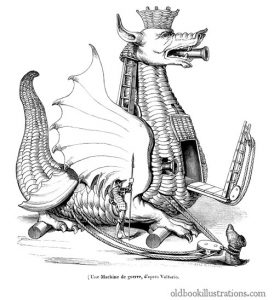
The Trojan Dragon
This beast allows you and up to six colleagues to safely teach behind two tons of armor, scales and non-functional wings. It comes with a remote-controlled drawbridge, an optional ladder, and a fire-belching steam whistle that signals the end of class as it burns away any roving virus particles. Because of its height (22 feet, 4 claws), it will not fit through the doorway of any building on campus. It is perfect for remote teaching, though, or for tying up near one of the remaining campus tents and surprising long-missing students who come close enough to investigate. It is fully outfitted with wifi, a microwave oven, a 5,000-meter extension cord, a chamber pot, and takeout menus from every restaurant in Lawrence.
Before you rush out and buy one of these high-fashion masks, we want to remind you to stay safe this semester. You know that, of course, but don’t let your guard down.
Also do what you can to make the semester as meaningful as possible, despite pandemic fatigue, brain fog, and voice-muffling protective gear. We have a wide array of resources on the CTE website and our Flexible Teaching website to help you and inspire you. We and the rest of the CTE staff and Faculty Fellows are also available to help however we can. Don’t be afraid to reach out, even if you are simply worried about whether it is permissible to wear a light-colored mask after Labor Day or whether the ear bands on your mask must always match your shoes. We don’t always have immediate answers, especially about fashion, but we can usually connect you with someone who does.
Now please excuse us. A crowd has gathered around the Trojan Dragon, and we sense an opportunity for learning.
What does higher ed do? Our answer may determine its future.
The future of higher education may very well hinge on our skill as interpreters and communicators.
Too often, though, we never bother to define the terms we use or to help students, parents, and employers understand the purpose and significance of a college education, Ashley Finley told participants at the 2021 KU Teaching Summit last week.

“We develop language as currency,” said Finley, who is vice president for research at the Association of American Colleges and Universities, “and we communicate with each other about a shared meaning without really ever actually defining” what we mean.
Finley is a sociologist who has studied such areas as assessment, high-impact practices, equity in institutional outcomes, and student success. In her presentation at the Teaching Summit, she drew on a recent AAC&U report she wrote titled How College Contributes to Workforce Success, based on a survey of executives and hiring managers at 496 companies. That report contains both good and bad news for colleges and universities.
For instance, 87% of executives and hiring managers said a degree was definitely or probably worth it, but a smaller percentage (67%) said they had a great deal or quite a lot of confidence in higher education. Finley compared those results to a random sample of adults who were asked the same question. Only 60% thought a college degree was worth the time and money.
“We have to get serious about how we’re communicating out what we do,” Finley said. Colleges and universities need to do better at telling their story, she said, not only to employers but to students.
“That explicitness is absolutely for our students,” she said. “They will be our best ambassadors.”
Finley used the term well-rounded as an example of why good communication is important. In academia, we often talk about a need for well-rounded students, but we rarely explain what that means. Students create their own interpretations, though, as Finley showed with a student quote from a focus group:
“I don’t know too many jobs that the job is being well-rounded. You know, it’s not like you’re going to work at Well-Rounded Inc. or something.”
Finley said she appreciated the student’s snark.
“They’ve taken us to task for not defining this thing that we lob in front of them constantly,” Finley said.
She also said the comment was a “good reality check” for educators, in part because of the connection the student made between education and employment.
“They linked it with a job, as if to suggest what you do for me as a person, how I situate myself in a community, and what I learn about a sense of purpose doesn’t have anything to do with the work that I’ll do,” Finley said.
Defining the common good
Another term we often fail to define, Finley said, is common good. She referred to the title of her presentation – Learning for Our Common Good: The Overlapping Skills of Successful Lives and Careers – and said that we all had different definitions of common good and that we rarely shared those definitions with others. She tried to unpack the term.

“When we are talking about a common good, we are talking about a greater purpose,” Finley said. “We are talking about how work influences our life, builds a sense of identity, gives our own sense of purpose in the world.”
The common good, she said, is closely tied to the overlapping skills we want students to acquire while they are in college. She asked members of the audience to offer their thoughts on those skills and on how students should be different by the time they graduate. The responses painted a broad picture of aspirations within the academy:
- To critically evaluate what they read and hear
- To gain perspectives on people and stories other than their own
- To be problem-solvers and “realize that there’s a whole big world out there”
- To be more open to diverse people and perspectives
- To try new things without fear of mistakes
- To feel empowered to make the world a better place
We all might add our own flavor and content to those things, Finley said, but they all sound perfectly reasonable for any discipline. She then asked:
“At the end of the day, can we in fact have a common conversation about what matters, and the standards to which we might hold ourselves for students’ learning and for their success?”
The employer view
Articulating a clearer sense of higher education will require us to move past the “false binaries” we often create, Finley said. Those include things like depth vs. breadth, and academic vs. practical skills. They all matter, she said. Higher education should be committed to knowledge, and “equally committed to the ways in which we equip students to have the skills to use knowledge, to create new knowledge, to have an imagination.”
Employers generally see the value in the many skills students gain in college, Finley said. They also value things like mindset, aptitudes, and character. The most recent AAC&U study showed a disconnect between the skills that colleges and universities emphasize and the views employers have on students’ career preparedness. When she and other researchers at AAC&U looked more closely at data from the employer survey, though, they found a stark difference in the perceptions of executives and hiring managers 40 and younger and those 50 and older. Those under 40 are more optimistic about student preparation. They also value different skills.
For instance, younger employers put considerably more emphasis on the need for critical thinking, leadership skills, empathy, and an ability to work with numbers and statistics. More broadly, they are far more likely than their older colleagues to say that a college education should encourage engagement in communities, foster a sense of social justice, focus on global issues, and emphasize the liberal arts and sciences.
“This felt like a game-changer to us,” Finley said, adding: “Hello, liberal arts. And hello, community-based learning.”
A need for articulation
If the views of younger employers offered optimism about the core values of higher education, another study that Finley brought up muddied the picture. That study showed a growing gap between the number of campuses that say they have learning outcomes and the number of students who are aware of those outcomes. She called that a “reality check of how our own communication is going.”

We have to increase the visibility of our core goals, Finley said. We have to do a better job of communicating, and we have to do a better job of projecting the type of outcomes we care about. This will require a nuanced approach to career preparation, she said, and must help students connect the dots among the courses they take and the experience they gain while in college. By the time students graduate, they should be different, she said.
“It’s not just about what they know and can do; it’s about who they are. And should they be able to persist through failure? Should they be a little more resilient? Should they have a sense of what it means to flourish?”
The answer to all of those is yes, of course, and Finley was optimistic that faculty could work through the many challenges before them.
“Good teachers are good learners,” Finley said. “You have to be humble to learn something new, and I hope that is always a point of connection we have with our students.”
* * * * * *
You will find a recording of Finley’s presentation at the Teaching Summit on the CTE website.
A weary campus asks: What happened to spring break?
As we near the halfway point of what we hope will be the final semester of remote everything, we at CTE encourage you to take a collective breath, put your feet up, and read an important news story you might have missed.
We can’t guarantee a happy ending. Then again, that all depends on what you consider happy.
Consider it the week that might have been.
LAWRENCE, Kan. (Coronavirus News Service) – Thousands of bleary-eyed students and frazzled faculty members staggered through the University of Kansas campus this week in a desperate search for spring break. For most, the search ended blissfully in unscheduled naps.

It was estimated to be the largest socially distanced gathering in this once-vibrant college town since the physics department hosted the Oppenheimer Memorial Baked Bean Blastoff in 1968. Masks were mandatory at that event, too.
Students dressed in flip-flops and neon yellow Give Me a Break! T-shirts crawled through bushes, wandered in circles around Wescoe Beach, and waded into Potter Lake looking for anything that resembled a break. Several dozen freshmen hopped on one foot and held open plastic shopping bags beneath trees in Marvin Grove, emulating a viral TikTok video that demonstrated “the proper method of catching a break.” The students said they had never actually seen a spring break, though, and admitted that they wouldn’t know one even if it fell into their bags.
At Watson and Anschutz Libraries, librarians dragging beach towels and wearing We Brake for Break masks scoured the stacks. Faculty members spent hours squinting into tea-stained mugs for clues. One distraught professor was found wrapped in paper towels in a Budig Hall rest room, sobbing something that sounded like “Rosebud.” Only the anthropology faculty seemed to understand the significance of the strange occurrences. One professor proclaimed it “the greatest day since Goodall picked up a pair of binoculars, or maybe since Geertz tried to nail jelly to a wall.”
Mass napping and an emergency task force
At the corner of Crescent Road and Naismith Drive, employees of McLain’s Market handed out Break Break Breakety Break Survival Kits, which were really gallon buckets of industrial-strength coffee beans and instructions that read: “Stuff as many beans into mouth as possible. Don’t try to talk. Just think happy thoughts.”
On the other side of campus, students rubbed fake beach sand into their hair and twirled tiny umbrellas between their fingers as they staked out socially distanced plots on the lawn near Watson Library, propped themselves up along the foundation of Fraser Hall, and took seats inside a tent outside Stauffer-Flint Hall. The muted stimulation proved overpowering, and most resorted to napping wherever they could find a spot.
When asked whether anyone had found spring break, most students just gave confused stares and nodded off. One student who seemed to have been appointed the group’s media representative issued a terse statement:
“Huh?”
In a press release, the interim assistant sub-vice chancellor for calendar efficiency said that all available employees in that one-person office were “diligently searching for spring break.”
“I think we canceled break, but I’m not sure,” the interim assistant sub-vice chancellor said. “We were all really tired when we talked about that last year, and everybody just wanted to get off Zoom. Whatever we did seemed like a good idea at the time.”
An emergency task force has been formed to study the problem.
The Center for Teaching Excellence responded to the crisis by sending out suggestions to beleaguered instructors. Among them were:
Allow catch-up time. Jennifer Delgado in physics created a “spring pause” for her classes, holding off on new assignments and allowing students to catch up on previous work. Lisa McLendon in journalism and mass communications did something similar, creating a “catch-up week” in her classes. Those seemingly small actions can offer students some temporary relief and buoy spirits.
Create lighthearted activities. Things like learning games, a question of the day, and self-care activities can help pull students from a midterm slumber and give classes a fresh focus. Also consider activities like scavenger hunts, which give students an opportunity to get away from their screens. CTE’s Flexible Teaching Guide offers many other suggestions.
Acknowledge the challenges. Let students know that you understand the challenges that a year of social distancing and mostly remote learning have created. Encourage them to take some time for themselves, give them permission to nap (when they aren’t in class), and find ways to help them interact. For instance, create random breakout rooms on Zoom or take a few minutes in class and encourage students to share what they wish they could be doing if they had an actual spring break. (Dreaming is a good thing.)
Take care of yourself. Students pick up on your moods. If you are sluggish and cranky, your students will be, too. So give yourself permission to get away you’re your computer. Visit the Spencer Museum of Art. Talk a walk through downtown Lawrence. Explore a part of campus you haven’t seen in a while. Visit the Baker Wetlands. Or just stroll through your neighborhood and look for signs of spring. Any of those things can lighten your mood and help make class go more smoothly for everyone.
When will break return?
Spring break is expected to return next year, although the interim assistant sub-vice chancellor for calendar efficiency said departments and schools had been asked to plan for three contingencies: Breaks that would last either 1 day; 1 hour, or 5 minutes.
When told that a five-minute spring break seemed ludicrous, the interim assistant sub-vice chancellor shrugged and said:
“We prefer to think of it as an abbreviated policy option necessitated by the constraints of time. You can call it whatever you want.”
(Note: This article does not reflect the views of KU, CTE, KU Libraries, the physics department, the anthropology department, McLain’s Market, the Office of the Interim Assistant Sub-Vice Chancellor for Calendar Efficiency, or anyone else you can think of. As far as we know, it’s not even true – except for the part about everyone missing spring break. Zzzzzz.)
GPAs at KU rose considerably in spring, a semester with an asterisk
Grade point averages for University of Kansas undergraduates rose an average of 8.4% in the spring as instructors offered more flexibility after a shift to remote teaching and more students took advantage of pass/fail grade options.
Men saw a slightly larger increase in GPAs than women did (9.1% vs. 7.9%), although women’s GPAs (3.3) were already higher than men’s (3.09) before the coronavirus pandemic. Freshmen had a larger increase in GPAs in the spring (10.7% for men; 10.5% for women). As with undergraduates as a whole, freshman women (3.05) already had higher GPAs than their male counterparts (2.8).
GPAs for graduate students rose 1.3%, to 3.86 from 3.81, and have remained within a small range over the past decade.
Compassion, accommodations and concern
Those GPA increases are hardly a surprise, and many aspects of the semester will carry an asterisk to explain the dramatic changes that took place during the pandemic.
“Flexibility” became the guiding principle as the world figured out how to live amid a deadly virus. For KU and other colleges and universities, that flexibility included adaptations to class format as campuses were closed, an extended window for withdrawal from classes, requests to avoid use of attendance as a factor in grades. broader use of pass/fail course options, additional time for online exams, and widespread pleas for compassion in grading. There were also concerns, many of which were validated, that some students were cheating during remote exams.
All of those factors no doubt played a role in pushing up grade point averages in the spring. Among the schools at KU, spring grades rose the most in architecture and design (11.3%), followed by engineering (10.6%), law (9.9%), liberal arts and sciences (9.8%), pharmacy (8.1%) and journalism and mass communications (6.9%). Schools with smaller increases already had GPAs higher than the university average: business, education, music, and social welfare. (See the chart below.)
The meaning of GPAs
I have no national data to compare with KU’s data, and I offer the statistics mostly as a point of interest.
I was surprised by how high the average GPA was in some fields even before spring of this year, but that could be the result of many things (including better student work and more openness to rewarding good work). Between 2010 and 2019, the average GPA at KU increased about 2%, although it rose the most in engineering (5.9%), liberal arts and sciences (5.9%), and music (3.8%).
When I look at GPAs in this context, though, I can’t help but wonder about bigger questions:
- What does a grade mean?
- What should it represent?
- Have grades outlived their usefulness? (GPAs are tied to credit hours, which have little or no meaning in a world of online and hybrid courses.)
- How are grades connected to actual learning?
In a book chapter titled “The Dangerous Myth of Grade Inflation,” Alfie Kohn says grades are too often seen in terms of a “marketplace analogy.” He asks: “Is the professor’s job to rate students like blenders for the convenience of corporations, or to offer feedback that will help students learn more skillfully and enthusiastically?”
In other words, how can we think less about grades and more about learning?