Most Americans still see a four-year degree as important, but it is not at the top of the list of things that will help someone achieve a successful career, a recent Heartland Monitor poll suggests.
In the poll, respondents ranked technology skills, an ability to work with diverse groups of people, keeping skills current, and having family connections above a four-year college degree.
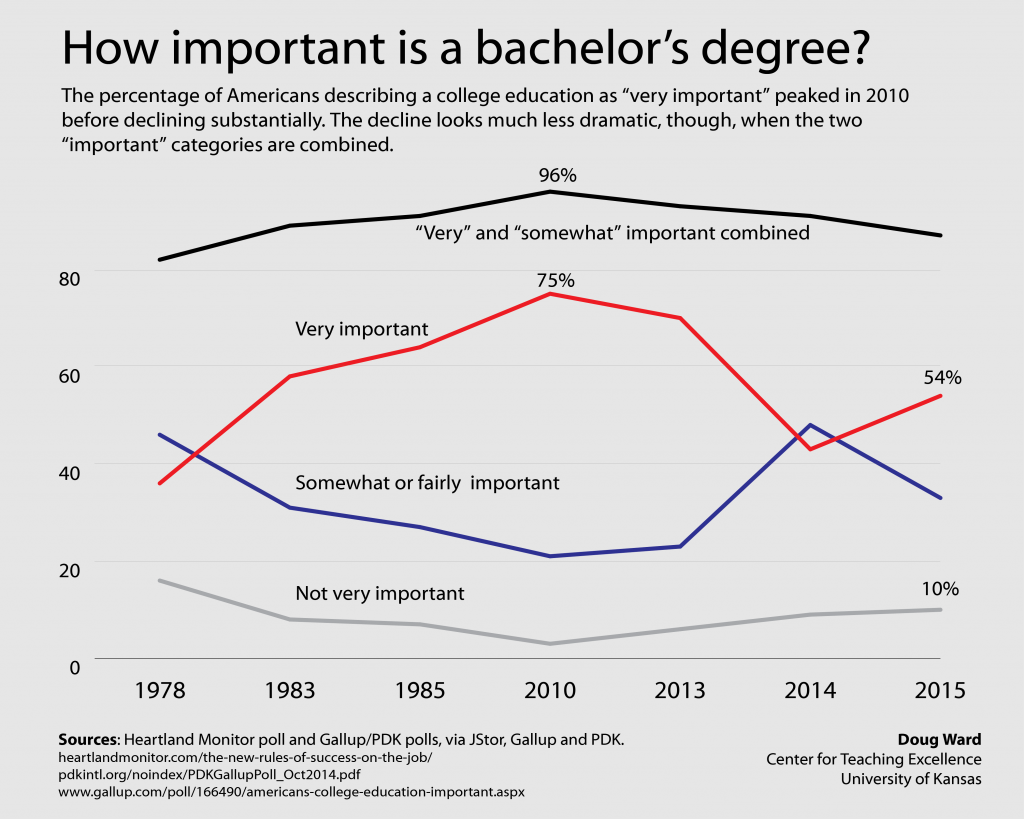
They certainly didn’t dismiss a college education. More than half said a college degree was very important and 87 percent said it was either very or somewhat important. Those between age 18 and 29 ranked the importance of a degree slightly higher than those 30 and over (55 percent vs. 53 percent). Blacks and Hispanics looked at a degree more favorably than did whites.
The poll was sponsored by National Journal, Allstate and The Atlantic. In interpreting the results, the organizations said the responses about college were “a startling admission in the United States, where college has long been seen as a Holy Grail to the good life.”
Maybe. In context, though, it doesn’t look so startling.
I pieced together data from the Heartland poll and several polls conducted by Gallup for the scholarly organization Phi Delta Kappa. (Most of those are available through the database JStore.) Polls in 1978, 1983, 1985, 2010, 2013, and 2014 asked a question about the importance of college very similar to the one asked in the Heartland poll.
Most certainly, the percentage of Americans saying that a degree is very important has declined substantially since a peak of 75 percent in 2010. If the categories for “very important” and “somewhat” or “fairly” important are combined, though, the decline isn’t nearly so steep.
Those combined totals rose from 82 percent in 1978 to a peak of 96 percent in 2010 before declining to 87 percent in 2015.
It is.
Most people still see a college degree as an important factor in achieving success on the job, yet they have also begun to look at other options, especially as a growing percentage of potential students delay their entrance to college for financial reasons.
Rather than stirring a panic for higher education, though, the polls add one more reason for colleges and universities to clean up their tarnished reputation.
The tech connection
Let’s dig a little deeper into the importance of technology skills.
In April, I wrote about a report from the Educational Testing Service that raised concerns about American millennials’ poor skills when compared with their counterparts around the world.
A report by a group of CEOs (There was a link, but the page no longer exists) offers its own evaluation of that and other data, saying that 58 percent of millennials lack the basic skills they need to solve problems with technology. This is even as millennials use digital media for 35 hours a week, on average, the report said.
The CEO group, which is called Change the Equation, says that this lack of technological know-how will diminish millennials’ job prospects, if it already hasn’t. Most millennials don’t seem to understand how their lack of skills is hurting them, the report said, although only 37 percent of employers say young workers are prepared to stay current with new technologies.
“We must make a point of incorporating technology into how students learn to tackle problems. This does not mean that every young person needs to become a computer scientist, though more certainly should. Instead, students must learn to realize the full potential of technology as a critical aid to human productivity and invention,” the report said.
I don’t dispute the importance of technological savviness. I push my students to use technology for problem-solving, and I emphasize the importance of digital literacy.
Technology isn’t magic, though. Yes, students need technological skills, but that means using hardware and software to solve problems, answer questions, test ideas, communicate solutions, build communities, and stretch our potential.
That all starts with critical thinking, which should be the primary focus of all education. We must incorporate technology into that process. Technology is simply a means to an end, though.
Briefly …
JStor, the online archive, has started a teaching newsletter aimed at helping instructors integrate JStor material into lesson plans. … Alison Phipps, director of gender studies at Sussex University, warns universities against pursuing easy scapegoats in the quest to reduce sexual assault and sexual harassment. In an article for The Guardian, she says “we must avoid enabling institutions to blame particular students or activities for problems they themselves have had a hand in creating.”
Tagged Education Matters, future of higher education, polls and surveys, research, teaching and technology